TransReg: Cross-transformer as auto-registration module for multi-view mammogram mass detection
Paper and Code
Nov 09, 2023

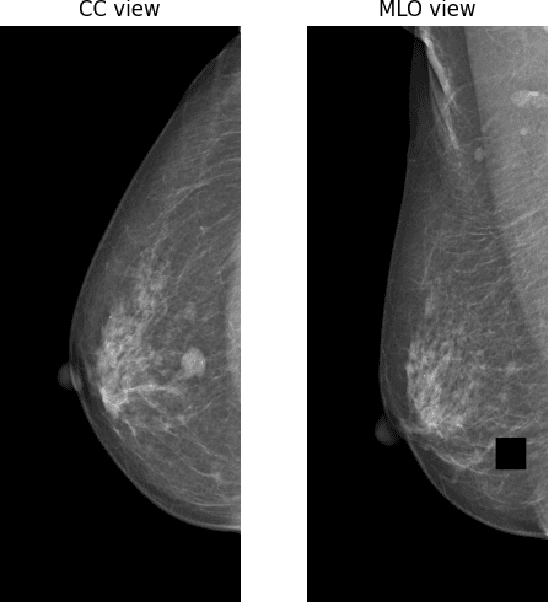

Screening mammography is the most widely used method for early breast cancer detection, significantly reducing mortality rates. The integration of information from multi-view mammograms enhances radiologists' confidence and diminishes false-positive rates since they can examine on dual-view of the same breast to cross-reference the existence and location of the lesion. Inspired by this, we present TransReg, a Computer-Aided Detection (CAD) system designed to exploit the relationship between craniocaudal (CC), and mediolateral oblique (MLO) views. The system includes cross-transformer to model the relationship between the region of interest (RoIs) extracted by siamese Faster RCNN network for mass detection problems. Our work is the first time cross-transformer has been integrated into an object detection framework to model the relation between ipsilateral views. Our experimental evaluation on DDSM and VinDr-Mammo datasets shows that our TransReg, equipped with SwinT as a feature extractor achieves state-of-the-art performance. Specifically, at the false positive rate per image at 0.5, TransReg using SwinT gets a recall at 83.3% for DDSM dataset and 79.7% for VinDr-Mammo dataset. Furthermore, we conduct a comprehensive analysis to demonstrate that cross-transformer can function as an auto-registration module, aligning the masses in dual-view and utilizing this information to inform final predictions. It is a replication diagnostic workflow of expert radiologists
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge