Transfer learning for non-intrusive load monitoring and appliance identification in a smart home
Paper and Code
Jan 08, 2023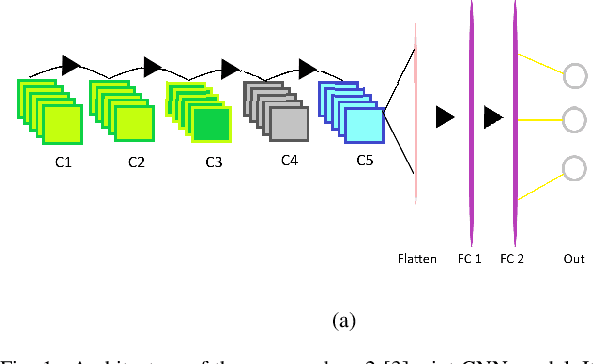


Non-intrusive load monitoring (NILM) or energy disaggregation is an inverse problem whereby the goal is to extract the load profiles of individual appliances, given an aggregate load profile of the mains of a home. NILM could help identify the power usage patterns of individual appliances in a home, and thus, could help realize novel energy conservation schemes for smart homes. In this backdrop, this work proposes a novel deep-learning approach to solve the NILM problem and a few related problems as follows. 1) We build upon the reputed seq2-point convolutional neural network (CNN) model to come up with the proposed seq2-[3]-point CNN model to solve the (home) NILM problem and site-NILM problem (basically, NILM at a smaller scale). 2) We solve the related problem of appliance identification by building upon the state-of-the-art (pre-trained) 2D-CNN models, i.e., AlexNet, ResNet-18, and DenseNet-121, which are trained upon two custom datasets that consist of Wavelets and short-time Fourier transform (STFT)-based 2D electrical signatures of the appliances. 3) Finally, we do some basic qualitative inference about an individual appliance's health by comparing the power consumption of the same appliance across multiple homes. Low-frequency REDD dataset is used to train and test the proposed deep learning models for all problems, except site-NILM where REFIT dataset has been used. As for the results, we achieve a maximum accuracy of 94.6\% for home-NILM, 81\% for site-NILM, and 88.9\% for appliance identification (with Resnet-based model).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge