Tracking Blobs in the Turbulent Edge Plasma of Tokamak Fusion Reactors
Paper and Code
Nov 16, 2021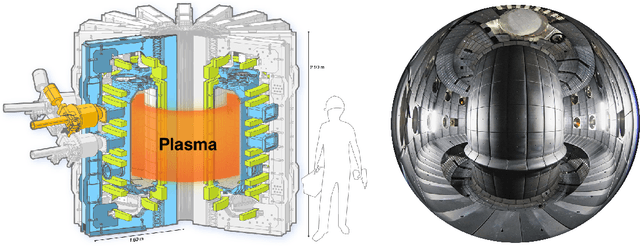
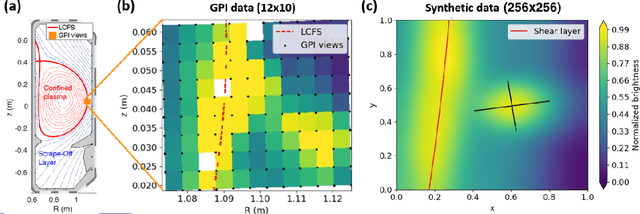
The analysis of turbulent flows is a significant area in fusion plasma physics. Current theoretical models quantify the degree of turbulence based on the evolution of certain plasma density structures, called blobs. In this work we track the shape and the position of these blobs in high frequency video data obtained from Gas Puff Imaging (GPI) diagnostics, by training a mask R-CNN model on synthetic data and testing on both synthetic and real data. As a result, our model effectively tracks blob structures on both synthetic and real experimental GPI data, showing its prospect as a powerful tool to estimate blob statistics linked with edge turbulence of the tokamak plasma.
* 8 pages, 9 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge