Towards Robust Learning-Based Pose Estimation of Noncooperative Spacecraft
Paper and Code
Sep 01, 2019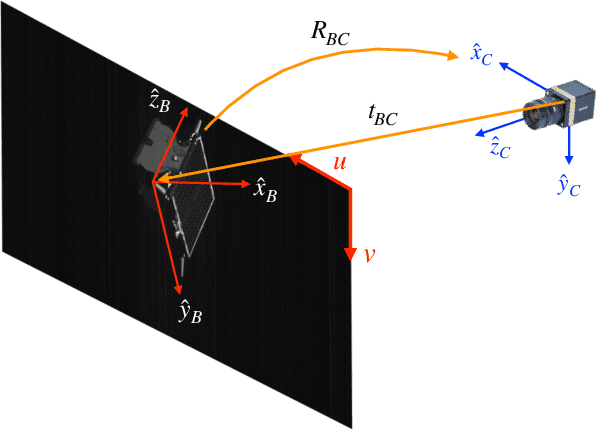

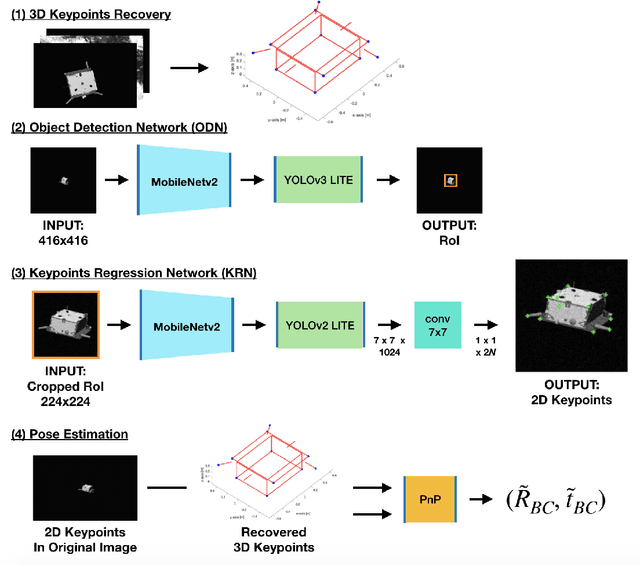

This work presents a novel Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture and a training procedure to enable robust and accurate pose estimation of a noncooperative spacecraft. First, a new CNN architecture is introduced that has scored a fourth place in the recent Pose Estimation Challenge hosted by Stanford's Space Rendezvous Laboratory (SLAB) and the Advanced Concepts Team (ACT) of the European Space Agency (ESA). The proposed architecture first detects the object by regressing a 2D bounding box, then a separate network regresses the 2D locations of the known surface keypoints from an image of the target cropped around the detected Region-of-Interest (RoI). In a single-image pose estimation problem, the extracted 2D keypoints can be used in conjunction with corresponding 3D model coordinates to compute relative pose via the Perspective-n-Point (PnP) problem. These keypoint locations have known correspondences to those in the 3D model, since the CNN is trained to predict the corners in a pre-defined order, allowing for bypassing the computationally expensive feature matching processes. This work also introduces and explores the texture randomization to train a CNN for spaceborne applications. Specifically, Neural Style Transfer (NST) is applied to randomize the texture of the spacecraft in synthetically rendered images. It is shown that using the texture-randomized images of spacecraft for training improves the network's performance on spaceborne images without exposure to them during training. It is also shown that when using the texture-randomized spacecraft images during training, regressing 3D bounding box corners leads to better performance on spaceborne images than regressing surface keypoints, as NST inevitably distorts the spacecraft's geometric features to which the surface keypoints have closer relation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge