Towards Robust Fine-grained Recognition by Maximal Separation of Discriminative Features
Paper and Code
Jun 10, 2020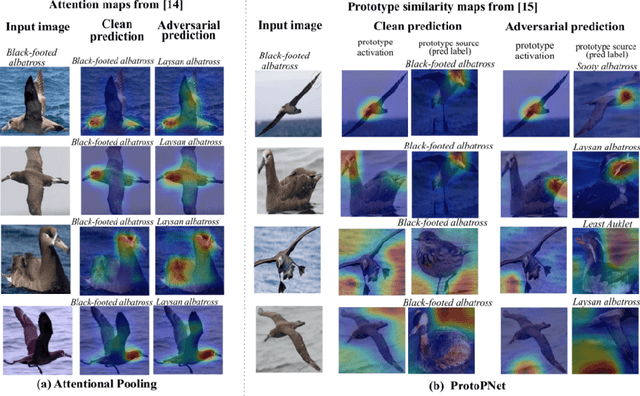
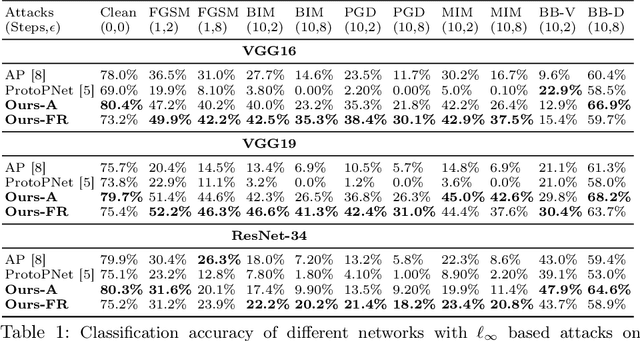
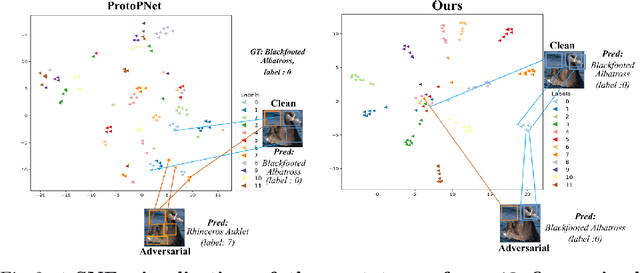
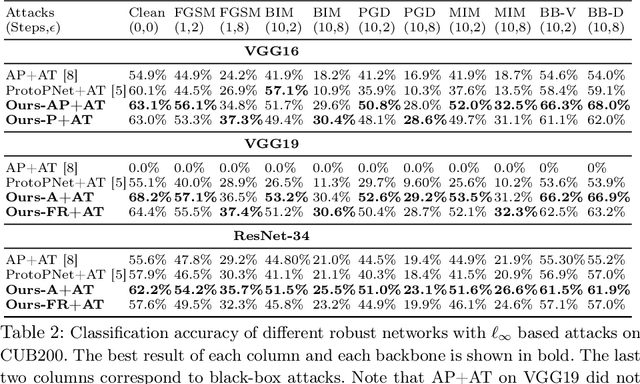
Adversarial attacks have been widely studied for general classification tasks, but remain unexplored in the context of fine-grained recognition, where the inter-class similarities facilitate the attacker's task. In this paper, we identify the proximity of the latent representations of different classes in fine-grained recognition networks as a key factor to the success of adversarial attacks. We therefore introduce an attention-based regularization mechanism that maximally separates the discriminative latent features of different classes while minimizing the contribution of the non-discriminative regions to the final class prediction. As evidenced by our experiments, this allows us to significantly improve robustness to adversarial attacks, to the point of matching or even surpassing that of adversarial training, but without requiring access to adversarial samples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge