Towards better healthcare: What could and should be automated?
Paper and Code
Oct 21, 2019
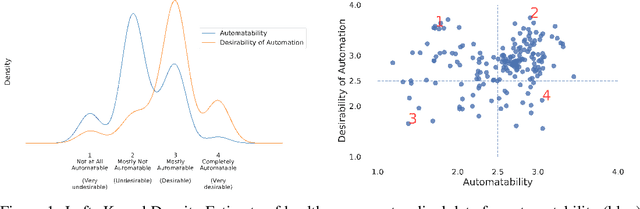
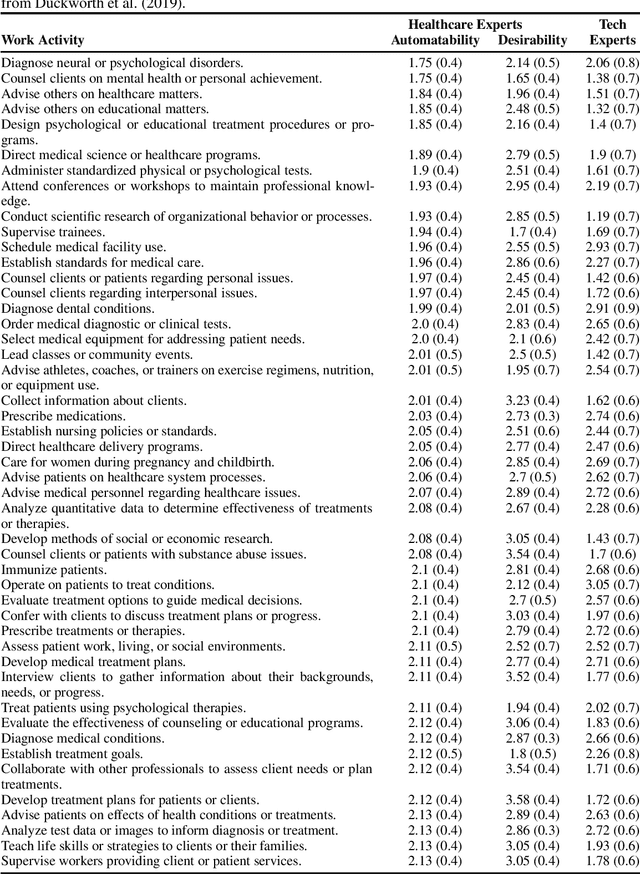
While artificial intelligence (AI) and other automation technologies might lead to enormous progress in healthcare, they may also have undesired consequences for people working in the field. In this interdisciplinary study, we capture empirical evidence of not only what healthcare work could be automated, but also what should be automated. We quantitatively investigate these research questions by utilizing probabilistic machine learning models trained on thousands of ratings, provided by both healthcare practitioners and automation experts. Based on our findings, we present an analytical tool (Automatability-Desirability Matrix) to support policymakers and organizational leaders in developing practical strategies on how to harness the positive power of automation technologies, while accompanying change and empowering stakeholders in a participatory fashion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge