Towards a Resilient Machine Learning Classifier -- a Case Study of Ransomware Detection
Paper and Code
Mar 13, 2020
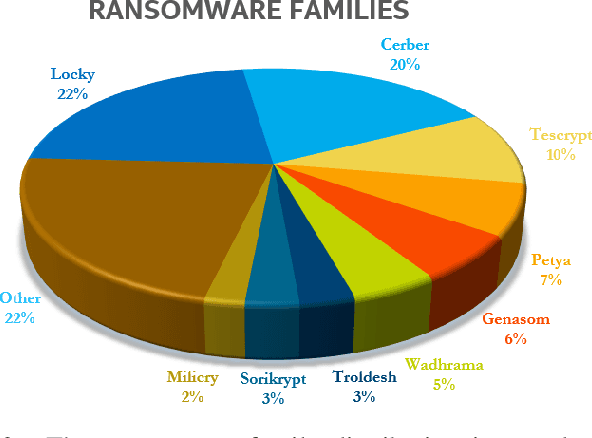


The damage caused by crypto-ransomware, due to encryption, is difficult to revert and cause data losses. In this paper, a machine learning (ML) classifier was built to early detect ransomware (called crypto-ransomware) that uses cryptography by program behavior. If a signature-based detection was missed, a behavior-based detector can be the last line of defense to detect and contain the damages. We find that input/output activities of ransomware and the file-content entropy are unique traits to detect crypto-ransomware. A deep-learning (DL) classifier can detect ransomware with a high accuracy and a low false positive rate. We conduct an adversarial research against the models generated. We use simulated ransomware programs to launch a gray-box analysis to probe the weakness of ML classifiers and to improve model robustness. In addition to accuracy and resiliency, trustworthiness is the other key criteria for a quality detector. Making sure that the correct information was used for inference is important for a security application. The Integrated Gradient method was used to explain the deep learning model and also to reveal why false negatives evade the detection. The approaches to build and to evaluate a real-world detector were demonstrated and discussed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge