Towards a quantitative assessment of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease
Paper and Code
Nov 06, 2020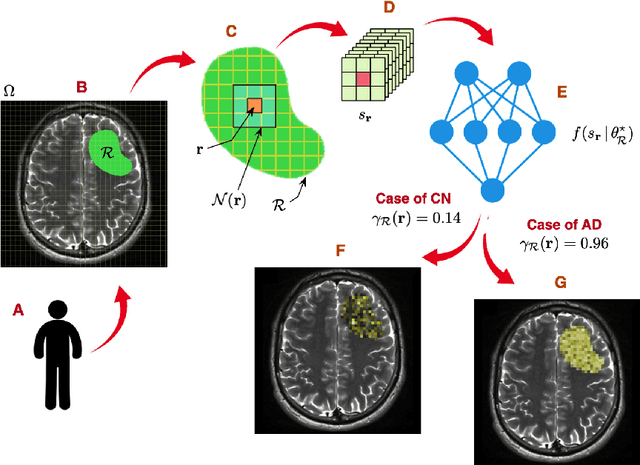

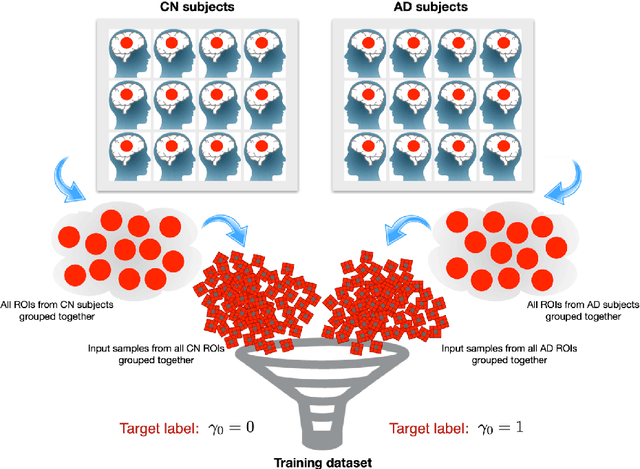

Alzheimer's disease (AD) is an irreversible neurodegenerative disorder that progressively destroys memory and other cognitive domains of the brain. While effective therapeutic management of AD is still in development, it seems reasonable to expect their prospective outcomes to depend on the severity of baseline pathology. For this reason, substantial research efforts have been invested in the development of effective means of non-invasive diagnosis of AD at its earliest possible stages. In pursuit of the same objective, the present paper addresses the problem of the quantitative diagnosis of AD by means of Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging (dMRI). In particular, the paper introduces the notion of a pathology specific imaging contrast (PSIC), which, in addition to supplying a valuable diagnostic score, can serve as a means of visual representation of the spatial extent of neurodegeneration. The values of PSIC are computed by a dedicated deep neural network (DNN), which has been specially adapted to the processing of dMRI signals. Once available, such values can be used for several important purposes, including stratification of study subjects. In particular, experiments confirm the DNN-based classification can outperform a wide range of alternative approaches in application to the basic problem of stratification of cognitively normal (CN) and AD subjects. Notwithstanding its preliminary nature, this result suggests a strong rationale for further extension and improvement of the explorative methodology described in this paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge