Toward Crowd-Sensitive Path Planning
Paper and Code
Oct 16, 2017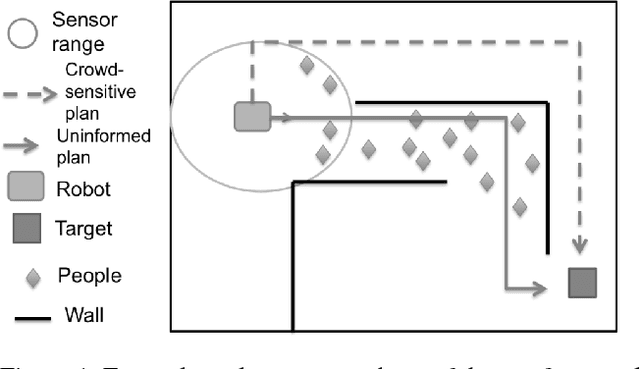
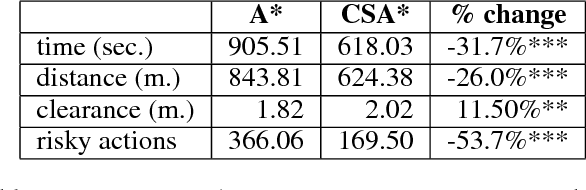

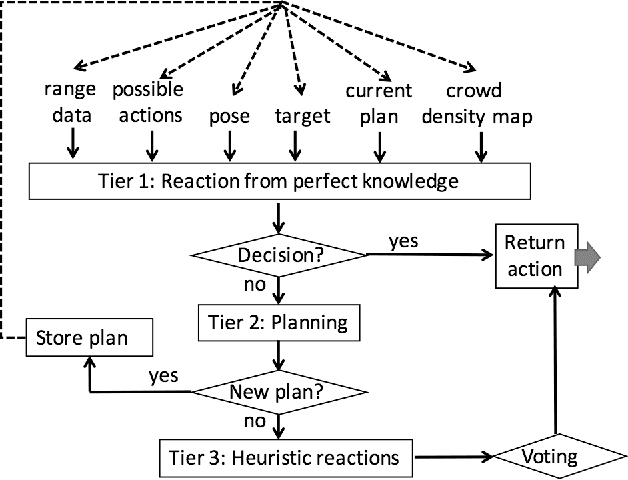
If a robot can predict crowds in parts of its environment that are inaccessible to its sensors, then it can plan to avoid them. This paper proposes a fast, online algorithm that learns average crowd densities in different areas. It also describes how these densities can be incorporated into existing navigation architectures. In simulation across multiple challenging crowd scenarios, the robot reaches its target faster, travels less, and risks fewer collisions than if it were to plan with the traditional A* algorithm.
* Accepted at AAAI fall symposium 2017
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge