Time series classification for predictive maintenance on event logs
Paper and Code
Nov 24, 2020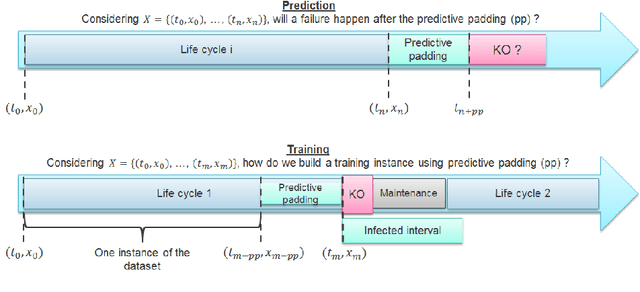
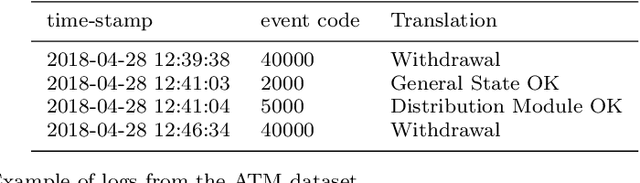
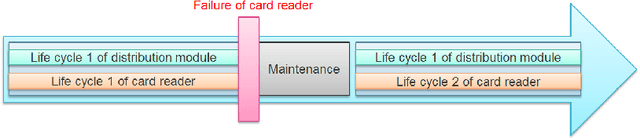
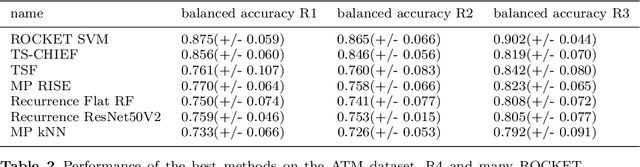
Time series classification (TSC) gained a lot of attention in the past decade and number of methods for representing and classifying time series have been proposed. Nowadays, methods based on convolutional networks and ensemble techniques represent the state of the art for time series classification. Techniques transforming time series to image or text also provide reliable ways to extract meaningful features or representations of time series. We compare the state-of-the-art representation and classification methods on a specific application, that is predictive maintenance from sequences of event logs. The contributions of this paper are twofold: introducing a new data set for predictive maintenance on automated teller machines (ATMs) log data and comparing the performance of different representation methods for predicting the occurrence of a breakdown. The problem is difficult since unlike the classic case of predictive maintenance via signals from sensors, we have sequences of discrete event logs occurring at any time and the lengths of the sequences, corresponding to life cycles, vary a lot.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge