Three Dogmas of Reinforcement Learning
Paper and Code
Jul 15, 2024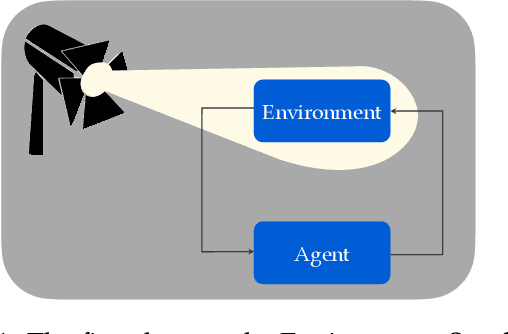
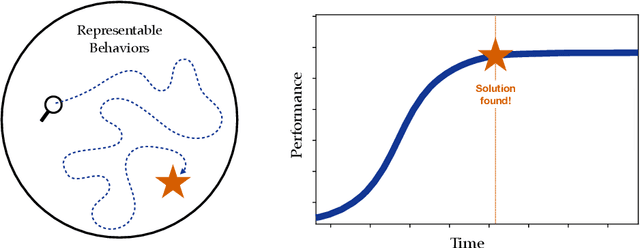
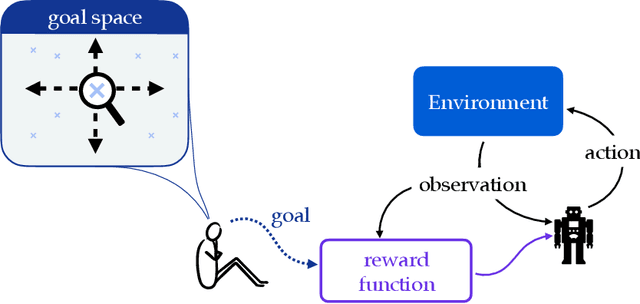
Modern reinforcement learning has been conditioned by at least three dogmas. The first is the environment spotlight, which refers to our tendency to focus on modeling environments rather than agents. The second is our treatment of learning as finding the solution to a task, rather than adaptation. The third is the reward hypothesis, which states that all goals and purposes can be well thought of as maximization of a reward signal. These three dogmas shape much of what we think of as the science of reinforcement learning. While each of the dogmas have played an important role in developing the field, it is time we bring them to the surface and reflect on whether they belong as basic ingredients of our scientific paradigm. In order to realize the potential of reinforcement learning as a canonical frame for researching intelligent agents, we suggest that it is time we shed dogmas one and two entirely, and embrace a nuanced approach to the third.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge