The use of deep learning in interventional radiotherapy : a review with a focus on open source and open data
Paper and Code
May 16, 2022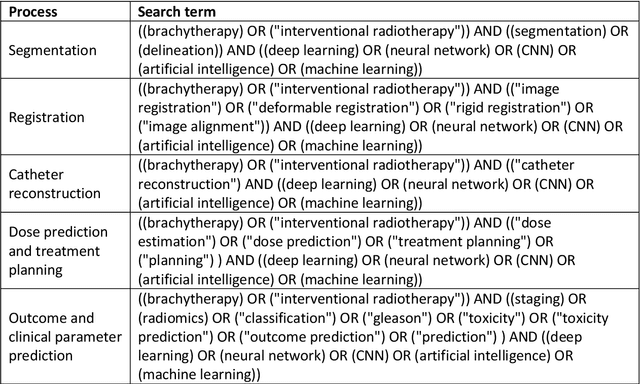
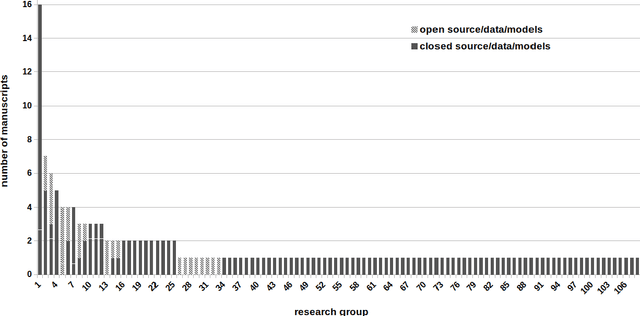
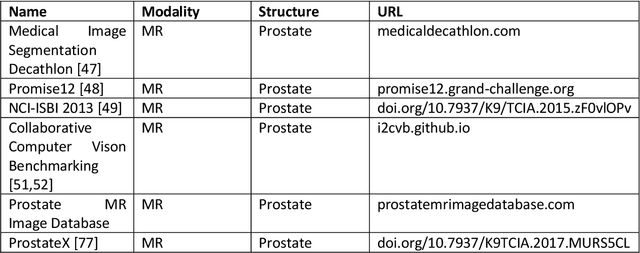
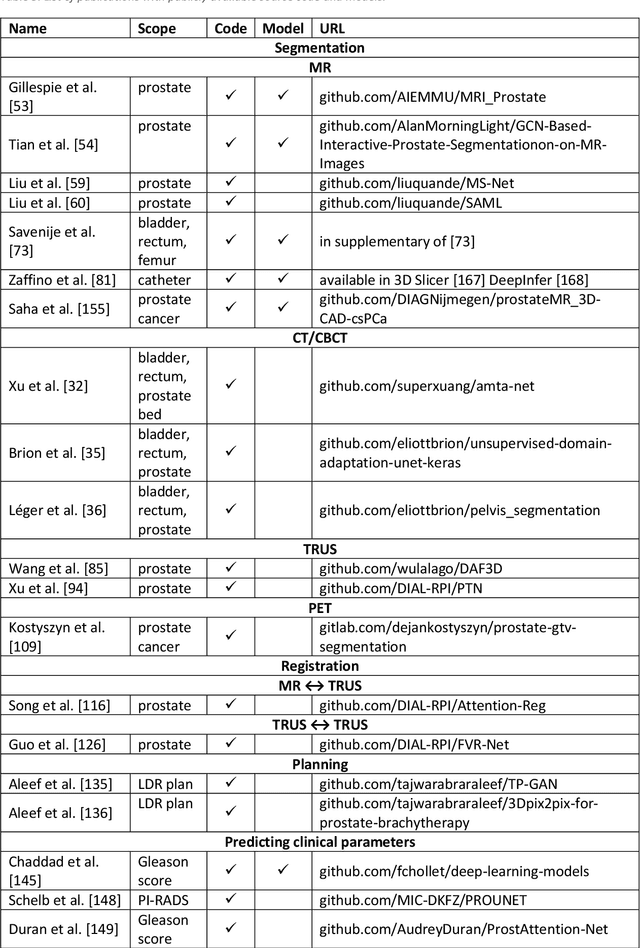
Deep learning advanced to one of the most important technologies in almost all medical fields. Especially in areas, related to medical imaging it plays a big role. However, in interventional radiotherapy (brachytherapy) deep learning is still in an early phase. In this review, first, we investigated and scrutinised the role of deep learning in all processes of interventional radiotherapy and directly related fields. Additionally we summarised the most recent developments. To reproduce results of deep learning algorithms both source code and training data must be available. Therefore, a second focus of this work was on the analysis of the availability of open source, open data and open models. In our analysis, we were able to show that deep learning plays already a major role in some areas of interventional radiotherapy, but is still hardly presented in others. Nevertheless, its impact is increasing with the years, partly self-propelled but also influenced by closely related fields. Open source, data and models are growing in number but are still scarce and unevenly distributed among different research groups. The reluctance in publishing code, data and models limits reproducibility and restricts evaluation to mono-institutional datasets. Summarised, deep learning will change positively the workflow of interventional radiotherapy but there is room for improvement when it comes to reproducible results and standardised evaluation methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge