The Effects of Hallucinations in Synthetic Training Data for Relation Extraction
Paper and Code
Oct 10, 2024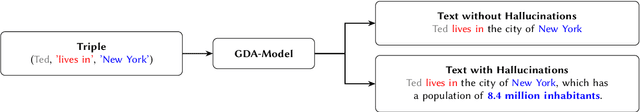
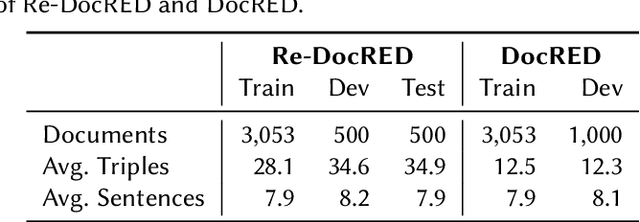
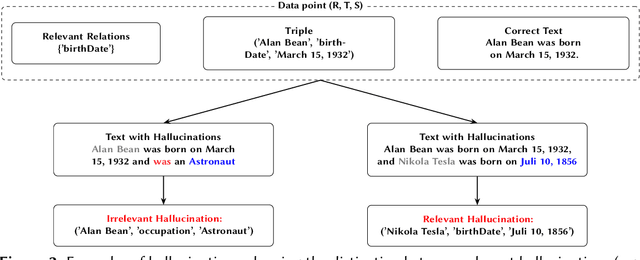
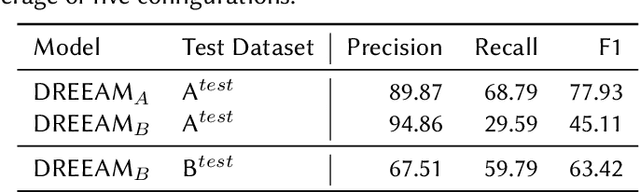
Relation extraction is crucial for constructing knowledge graphs, with large high-quality datasets serving as the foundation for training, fine-tuning, and evaluating models. Generative data augmentation (GDA) is a common approach to expand such datasets. However, this approach often introduces hallucinations, such as spurious facts, whose impact on relation extraction remains underexplored. In this paper, we examine the effects of hallucinations on the performance of relation extraction on the document and sentence levels. Our empirical study reveals that hallucinations considerably compromise the ability of models to extract relations from text, with recall reductions between 19.1% and 39.2%. We identify that relevant hallucinations impair the model's performance, while irrelevant hallucinations have a minimal impact. Additionally, we develop methods for the detection of hallucinations to improve data quality and model performance. Our approaches successfully classify texts as either 'hallucinated' or 'clean,' achieving high F1-scores of 83.8% and 92.2%. These methods not only assist in removing hallucinations but also help in estimating their prevalence within datasets, which is crucial for selecting high-quality data. Overall, our work confirms the profound impact of relevant hallucinations on the effectiveness of relation extraction models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge