Text and author-level political inference using heterogeneous knowledge representations
Paper and Code
Jun 24, 2022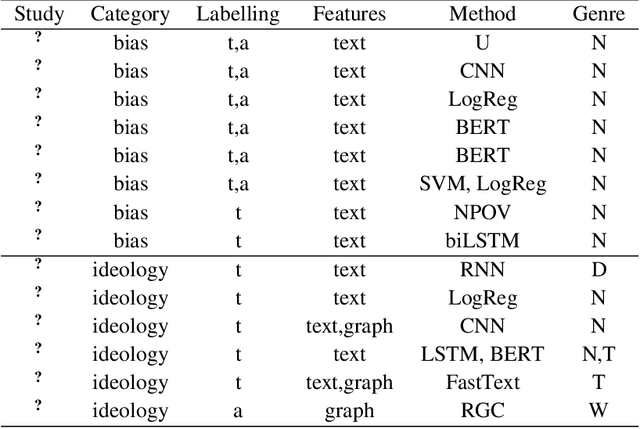


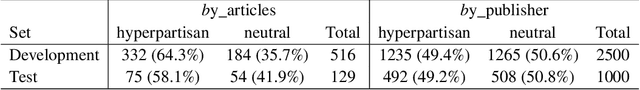
The inference of politically-charged information from text data is a popular research topic in Natural Language Processing (NLP) at both text- and author-level. In recent years, studies of this kind have been implemented with the aid of representations from transformers such as BERT. Despite considerable success, however, we may ask whether results may be improved even further by combining transformed-based models with additional knowledge representations. To shed light on this issue, the present work describes a series of experiments to compare alternative model configurations for political inference from text in both English and Portuguese languages. Results suggest that certain text representations - in particular, the combined use of BERT pre-trained language models with a syntactic dependency model - may outperform the alternatives across multiple experimental settings, making a potentially strong case for further research in the use of heterogeneous text representations in these and possibly other NLP tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge