Temporal Aware Deep Reinforcement Learning
Paper and Code
Sep 05, 2021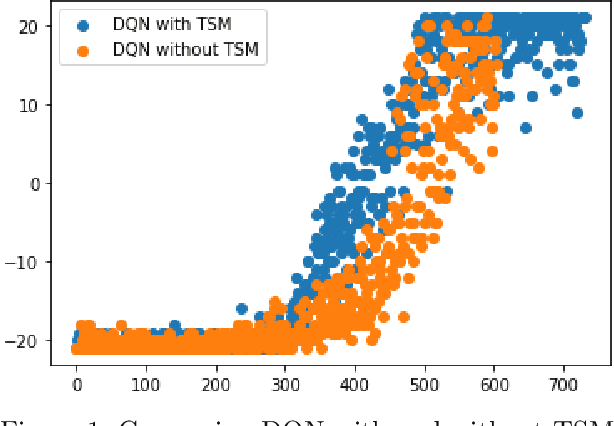
The function approximators employed by traditional image based Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) algorithms usually lack a temporal learning component and instead focus on learning the spatial component. We propose a technique wherein both temporal as well as spatial components are jointly learned. Our tested was tested with a generic DQN and it outperformed it in terms of maximum rewards as well as sample complexity. This algorithm has implications in the robotics as well as sequential decision making domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge