Synthetic Embedding-based Data Generation Methods for Student Performance
Paper and Code
Jan 03, 2021
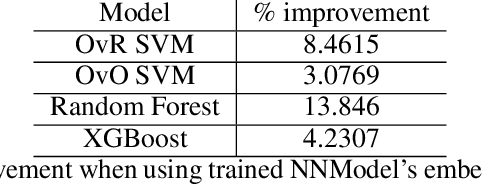
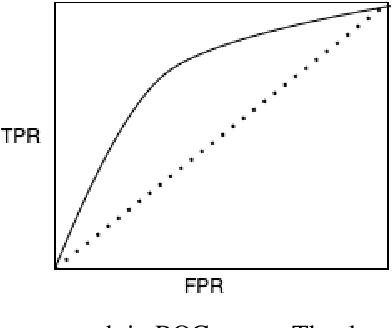
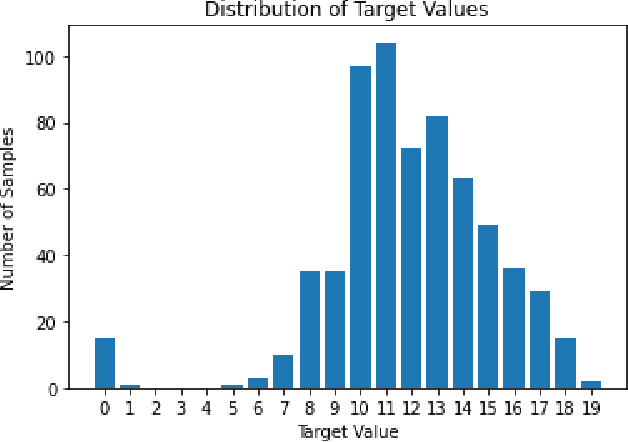
Given the inherent class imbalance issue within student performance datasets, samples belonging to the edges of the target class distribution pose a challenge for predictive machine learning algorithms to learn. In this paper, we introduce a general framework for synthetic embedding-based data generation (SEDG), a search-based approach to generate new synthetic samples using embeddings to correct the detriment effects of class imbalances optimally. We compare the SEDG framework to past synthetic data generation methods, including deep generative models, and traditional sampling methods. In our results, we find SEDG to outperform the traditional re-sampling methods for deep neural networks and perform competitively for common machine learning classifiers on the student performance task in several standard performance metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge