Swap distance minimization beyond entropy minimization in word order variation
Paper and Code
Apr 28, 2024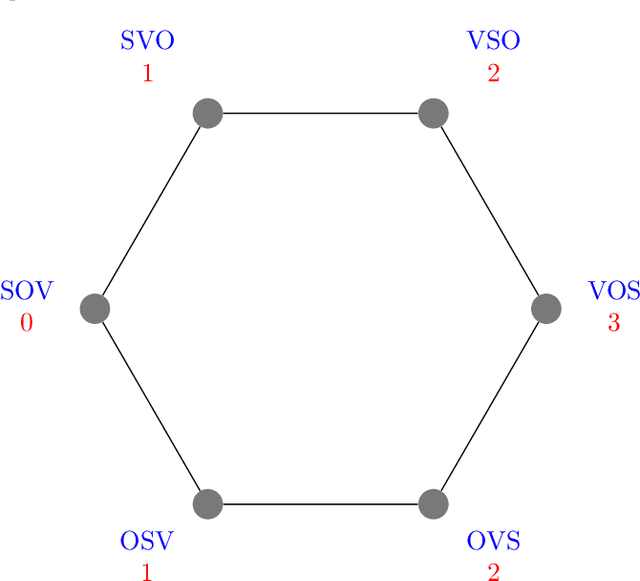
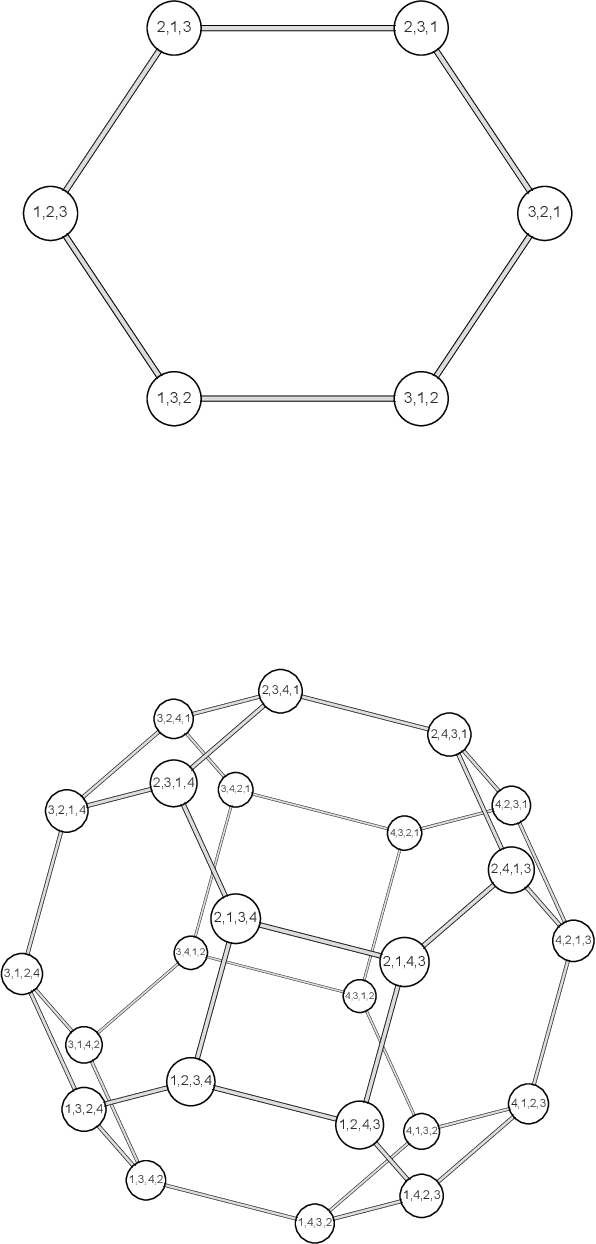

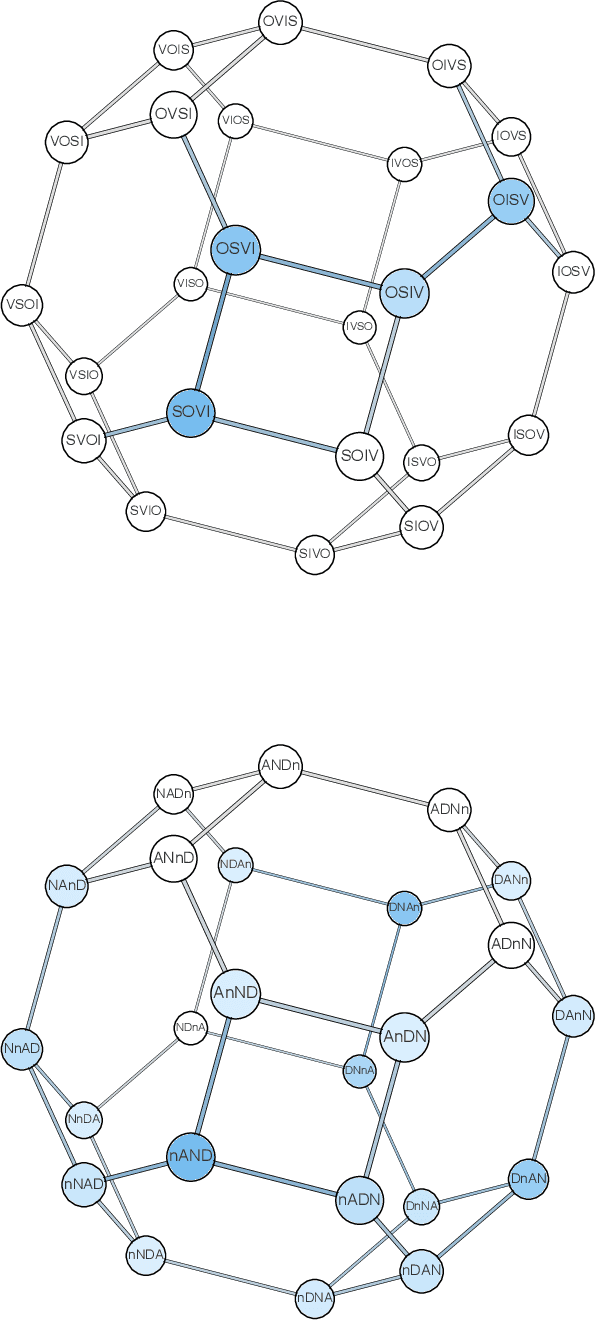
Here we consider the problem of all the possible orders of a linguistic structure formed by $n$ elements, for instance, subject, direct object and verb ($n=3$) or subject, direct object, indirect object and verb ($n=4$). We investigate if the frequency of the $n!$ possible orders is constrained by two principles. First, entropy minimization, a principle that has been suggested to shape natural communication systems at distinct levels of organization. Second, swap distance minimization, namely a preference for word orders that require fewer swaps of adjacent elements to be produced from a source order. Here we present average swap distance, a novel score for research on swap distance minimization, and investigate the theoretical distribution of that score for any $n$: its minimum and maximum values and its expected value in die rolling experiments or when the word order frequencies are shuffled. We investigate whether entropy and average swap distance are significantly small in distinct linguistic structures with $n=3$ or $n=4$ in agreement with the corresponding minimization principles. We find strong evidence of entropy minimization and swap distance minimization with respect to a die rolling experiment. The evidence of these two forces with respect to a Polya urn process is strong for $n=4$ but weaker for $n=3$. We still find evidence of swap distance minimization when word order frequencies are shuffled, indicating that swap distance minimization effects are beyond pressure to minimize word order entropy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge