Super-Wideband Massive MIMO
Paper and Code
Aug 02, 2022
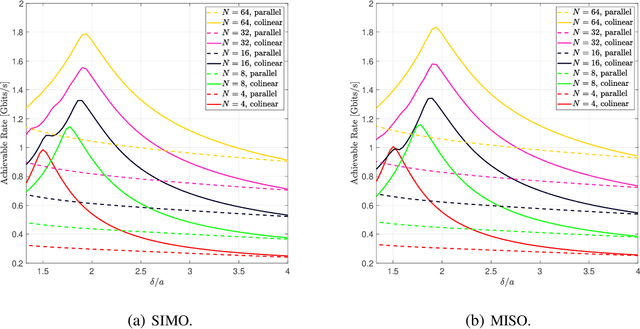
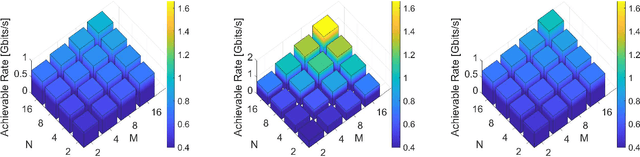
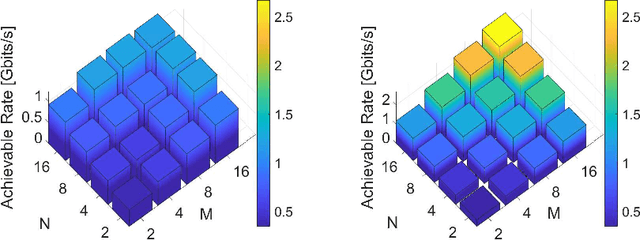
We present a unified model for connected antenna arrays with a massive (but finite) number of tightly integrated (i.e., coupled) antennas in a compact space within the context of massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) communication. We refer to this system as tightly-coupled massive MIMO. From an information-theoretic perspective, scaling the design of tightly-coupled massive MIMO systems in terms of the number of antennas, the operational bandwidth, and form factor was not addressed in prior art and hence not clearly understood. We investigate this open research problem using a physically consistent modeling approach for far-field (FF) MIMO communication based on multi-port circuit theory. In doing so, we turn mutual coupling (MC) from a foe to a friend of MIMO systems design, thereby challenging a basic percept in antenna systems engineering that promotes MC mitigation/compensation. We show that tight MC widens the operational bandwidth of antenna arrays thereby unleashing a missing MIMO gain that we coin "bandwidth gain". Furthermore, we derive analytically the asymptotically optimum spacing-to-antenna-size ratio by establishing a condition for tight coupling in the limit of large-size antenna arrays with quasi-continuous apertures. We also optimize the antenna array size while maximizing the achievable rate under fixed transmit power and inter-element spacing. Then, we study the impact of MC on the achievable rate of MIMO systems under light-of-sight (LoS) and Rayleigh fading channels. These results reveal new insights into the design of tightly-coupled massive antenna arrays as opposed to the widely-adopted "disconnected" designs that disregard MC by putting faith in the half-wavelength spacing rule.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge