Sublinear Time Algorithms for Several Geometric Optimization (With Outliers) Problems In Machine Learning
Paper and Code
Jan 07, 2023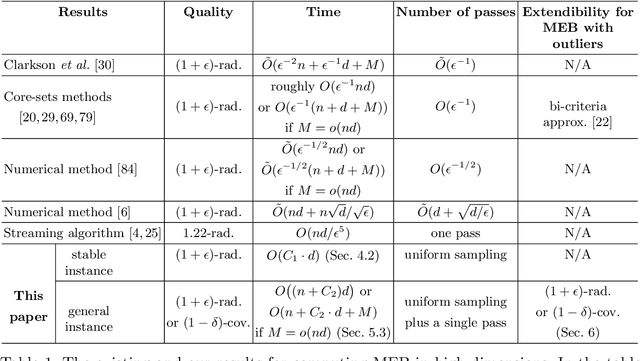
In this paper, we study several important geometric optimization problems arising in machine learning. First, we revisit the Minimum Enclosing Ball (MEB) problem in Euclidean space $\mathbb{R}^d$. The problem has been extensively studied before, but real-world machine learning tasks often need to handle large-scale datasets so that we cannot even afford linear time algorithms. Motivated by the recent studies on {\em beyond worst-case analysis}, we introduce the notion of stability for MEB, which is natural and easy to understand. Roughly speaking, an instance of MEB is stable, if the radius of the resulting ball cannot be significantly reduced by removing a small fraction of the input points. Under the stability assumption, we present two sampling algorithms for computing radius-approximate MEB with sample complexities independent of the number of input points $n$. In particular, the second algorithm has the sample complexity even independent of the dimensionality $d$. We also consider the general case without the stability assumption. We present a hybrid algorithm that can output either a radius-approximate MEB or a covering-approximate MEB. Our algorithm improves the running time and the number of passes for the previous sublinear MEB algorithms. Our method relies on two novel techniques, the Uniform-Adaptive Sampling method and Sandwich Lemma. Furthermore, we observe that these two techniques can be generalized to design sublinear time algorithms for a broader range of geometric optimization problems with outliers in high dimensions, including MEB with outliers, one-class and two-class linear SVMs with outliers, $k$-center clustering with outliers, and flat fitting with outliers. Our proposed algorithms also work fine for kernels.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge