Study of cognitive component of auditory attention to natural speech events
Paper and Code
Dec 19, 2023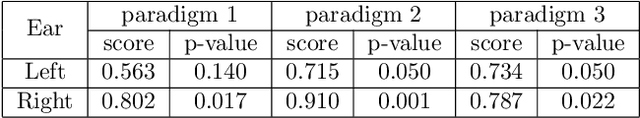
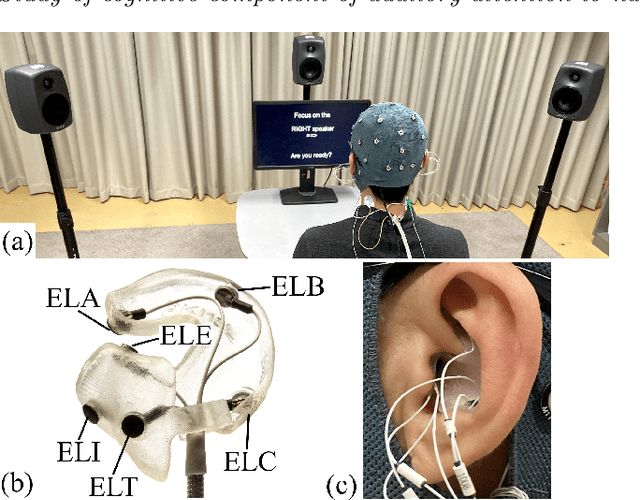
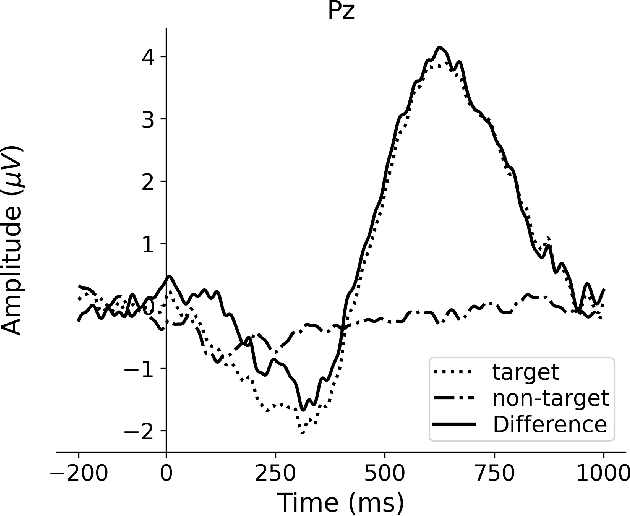
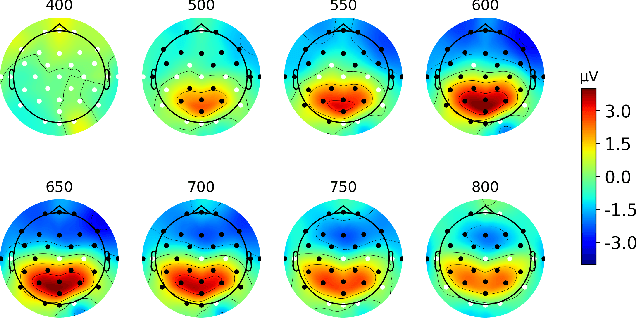
Event-related potentials (ERP) have been used to address a wide range of research questions in neuroscience and cognitive psychology including selective auditory attention. The recent progress in auditory attention decoding (AAD) methods is based on algorithms that find a relation between the audio envelope and the neurophysiological response. The most popular approach is based on the reconstruction of the audio envelope based on EEG signals. However, these methods are mainly based on the neurophysiological entrainment to physical attributes of the sensory stimulus and are generally limited by a long detection window. This study proposes a novel approach to auditory attention decoding by looking at higher-level cognitive responses to natural speech. To investigate if natural speech events elicit cognitive ERP components and how these components are affected by attention mechanisms, we designed a series of four experimental paradigms with increasing complexity: a word category oddball paradigm, a word category oddball paradigm with competing speakers, and competing speech streams with and without specific targets. We recorded the electroencephalogram (EEG) from 32 scalp electrodes and 12 in-ear electrodes (ear-EEG) from 24 participants. A cognitive ERP component, which we believe is related to the well-known P3b component, was observed at parietal electrode sites with a latency of approximately 620 ms. The component is statistically most significant for the simplest paradigm and gradually decreases in strength with increasing complexity of the paradigm. We also show that the component can be observed in the in-ear EEG signals by using spatial filtering. The cognitive component elicited by auditory attention may contribute to decoding auditory attention from electrophysiological recordings and its presence in the ear-EEG signals is promising for future applications within hearing aids.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge