Structural Optimization Ambiguity and Simplicity Bias in Unsupervised Neural Grammar Induction
Paper and Code
Jul 23, 2024


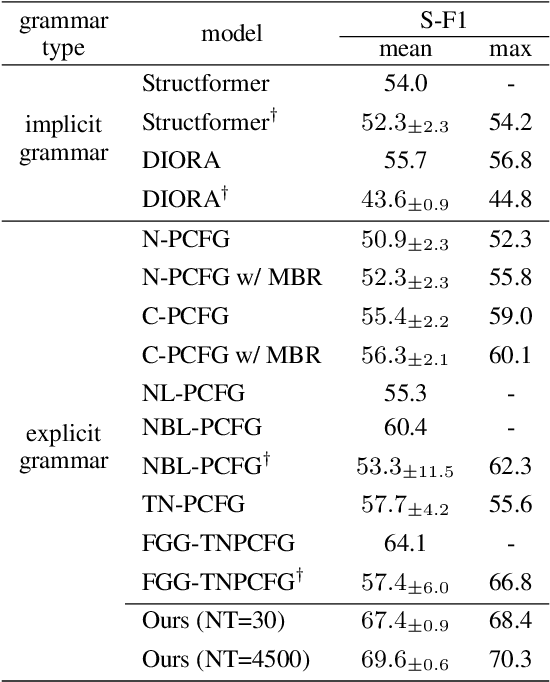
Neural parameterization has significantly advanced unsupervised grammar induction. However, training these models with a traditional likelihood loss for all possible parses exacerbates two issues: 1) $\textit{structural optimization ambiguity}$ that arbitrarily selects one among structurally ambiguous optimal grammars despite the specific preference of gold parses, and 2) $\textit{structural simplicity bias}$ that leads a model to underutilize rules to compose parse trees. These challenges subject unsupervised neural grammar induction (UNGI) to inevitable prediction errors, high variance, and the necessity for extensive grammars to achieve accurate predictions. This paper tackles these issues, offering a comprehensive analysis of their origins. As a solution, we introduce $\textit{sentence-wise parse-focusing}$ to reduce the parse pool per sentence for loss evaluation, using the structural bias from pre-trained parsers on the same dataset. In unsupervised parsing benchmark tests, our method significantly improves performance while effectively reducing variance and bias toward overly simplistic parses. Our research promotes learning more compact, accurate, and consistent explicit grammars, facilitating better interpretability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge