Strategy Extraction in Single-Agent Games
Paper and Code
May 22, 2023
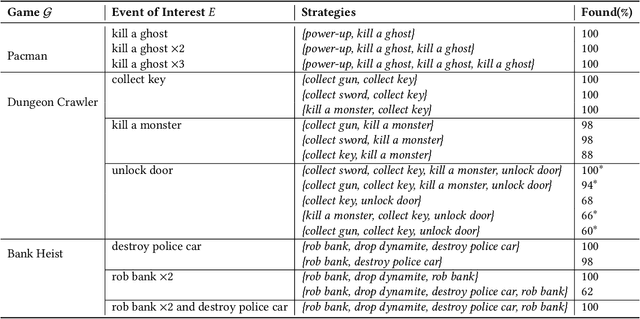


The ability to continuously learn and adapt to new situations is one where humans are far superior compared to AI agents. We propose an approach to knowledge transfer using behavioural strategies as a form of transferable knowledge influenced by the human cognitive ability to develop strategies. A strategy is defined as a partial sequence of events - where an event is both the result of an agent's action and changes in state - to reach some predefined event of interest. This information acts as guidance or a partial solution that an agent can generalise and use to make predictions about how to handle unknown observed phenomena. As a first step toward this goal, we develop a method for extracting strategies from an agent's existing knowledge that can be applied in multiple contexts. Our method combines observed event frequency information with local sequence alignment techniques to find patterns of significance that form a strategy. We show that our method can identify plausible strategies in three environments: Pacman, Bank Heist and a dungeon-crawling video game. Our evaluation serves as a promising first step toward extracting knowledge for generalisation and, ultimately, transfer learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge