States of confusion: Eye and Head tracking reveal surgeons' confusion during arthroscopic surgery
Paper and Code
Jun 11, 2021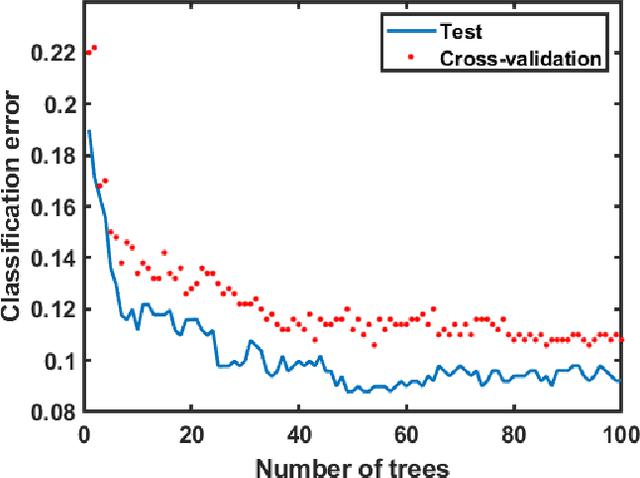
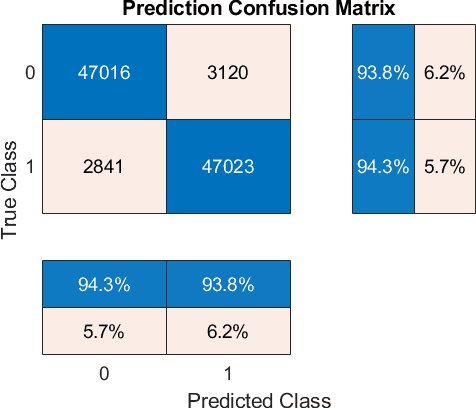

During arthroscopic surgeries, surgeons are faced with challenges like cognitive re-projection of the 2D screen output into the 3D operating site or navigation through highly similar tissue. Training of these cognitive processes takes much time and effort for young surgeons, but is necessary and crucial for their education. In this study we want to show how to recognize states of confusion of young surgeons during an arthroscopic surgery, by looking at their eye and head movements and feeding them to a machine learning model. With an accuracy of over 94\% and detection speed of 0.039 seconds, our model is a step towards online diagnostic and training systems for the perceptual-cognitive processes of surgeons during arthroscopic surgeries.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge