Speech Separation based on Contrastive Learning and Deep Modularization
Paper and Code
May 18, 2023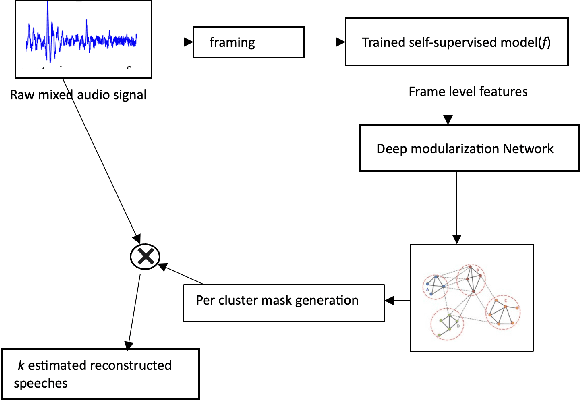
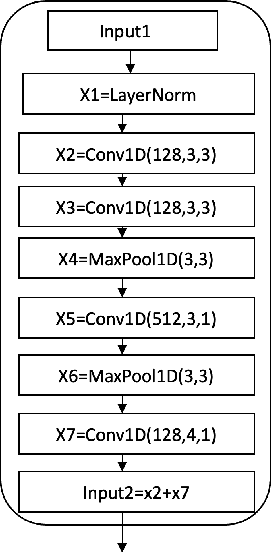
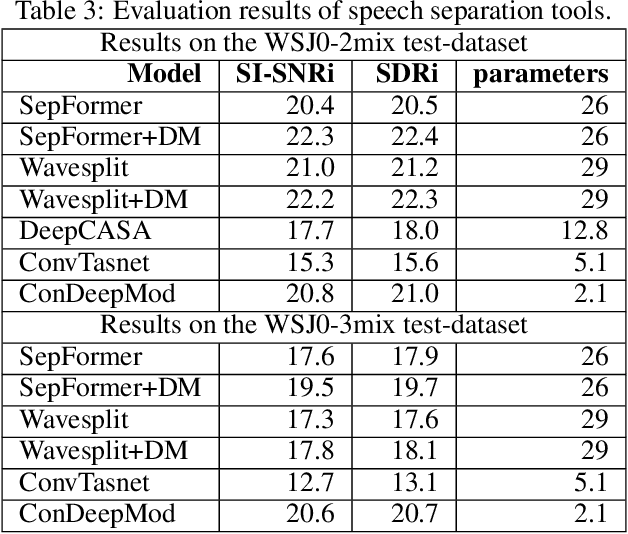
The current monaural state of the art tools for speech separation relies on supervised learning. This means that they must deal with permutation problem, they are impacted by the mismatch on the number of speakers used in training and inference. Moreover, their performance heavily relies on the presence of high-quality labelled data. These problems can be effectively addressed by employing a fully unsupervised technique for speech separation. In this paper, we use contrastive learning to establish the representations of frames then use the learned representations in the downstream deep modularization task. Concretely, we demonstrate experimentally that in speech separation, different frames of a speaker can be viewed as augmentations of a given hidden standard frame of that speaker. The frames of a speaker contain enough prosodic information overlap which is key in speech separation. Based on this, we implement a self-supervised learning to learn to minimize the distance between frames belonging to a given speaker. The learned representations are used in a downstream deep modularization task to cluster frames based on speaker identity. Evaluation of the developed technique on WSJ0-2mix and WSJ0-3mix shows that the technique attains SI-SNRi and SDRi of 20.8 and 21.0 respectively in WSJ0-2mix. In WSJ0-3mix, it attains SI-SNRi and SDRi of 20.7 and 20.7 respectively in WSJ0-2mix. Its greatest strength being that as the number of speakers increase, its performance does not degrade significantly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge