Spectrum Monitoring for Radar Bands using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Paper and Code
May 01, 2017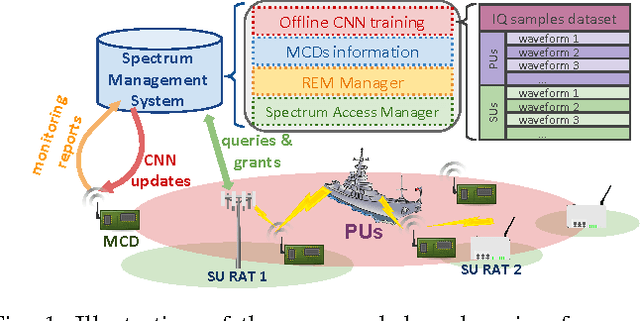
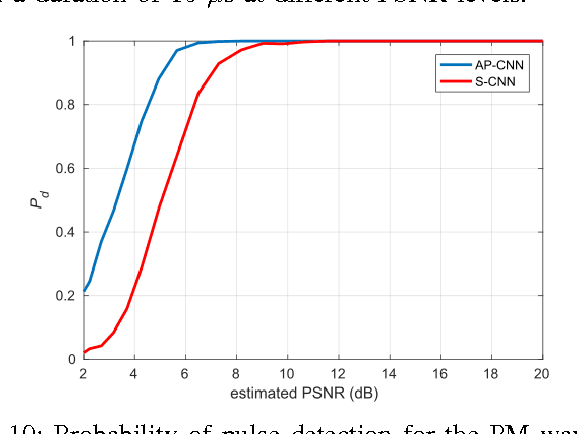
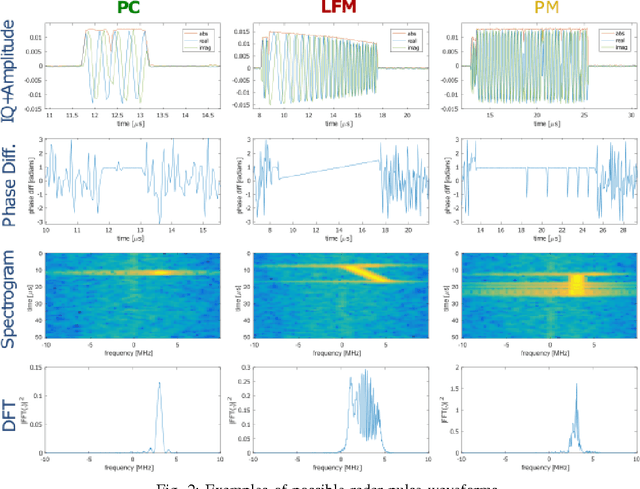
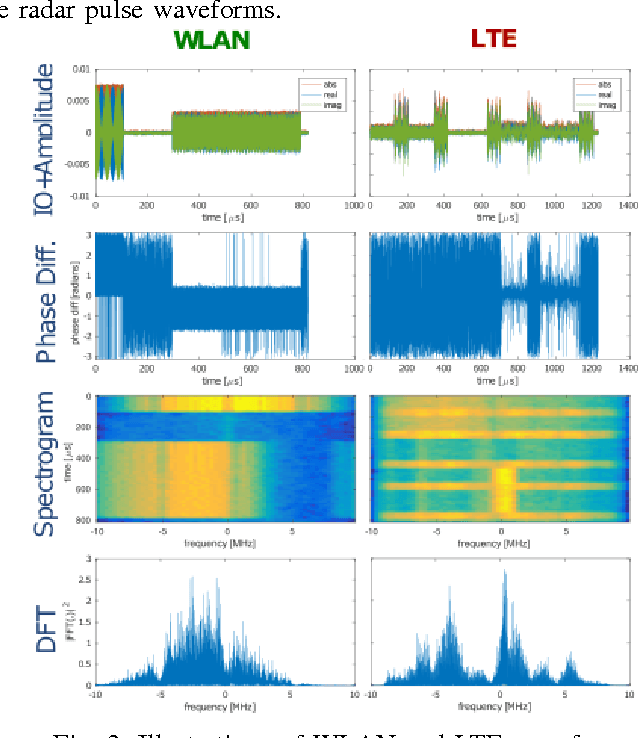
In this paper, we present a spectrum monitoring framework for the detection of radar signals in spectrum sharing scenarios. The core of our framework is a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) model that enables Measurement Capable Devices to identify the presence of radar signals in the radio spectrum, even when these signals are overlapped with other sources of interference, such as commercial LTE and WLAN. We collected a large dataset of RF measurements, which include the transmissions of multiple radar pulse waveforms, downlink LTE, WLAN, and thermal noise. We propose a pre-processing data representation that leverages the amplitude and phase shifts of the collected samples. This representation allows our CNN model to achieve a classification accuracy of 99.6% on our testing dataset. The trained CNN model is then tested under various SNR values, outperforming other models, such as spectrogram-based CNN models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge