Spectral Image Segmentation with Global Appearance Modeling
Paper and Code
Jun 11, 2020
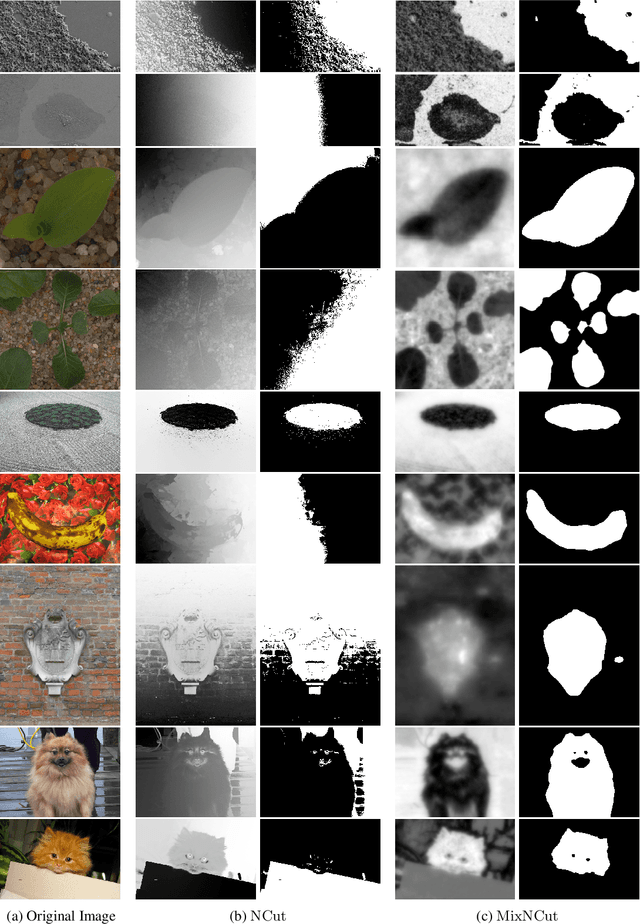
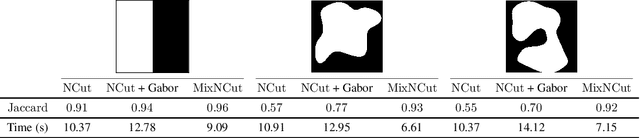


We introduce a new spectral method for image segmentation that incorporates long range relationships for global appearance modeling. The approach combines two different graphs, one is a sparse graph that captures spatial relationships between nearby pixels and another is a dense graph that captures pairwise similarity between all pairs of pixels. We extend the spectral method for Normalized Cuts to this setting by combining the transition matrices of Markov chains associated with each graph. We also derive an efficient method that uses importance sampling for sparsifying the dense graph of appearance relationships. This leads to a practical algorithm for segmenting high-resolution images. The resulting method can segment challenging images without any filtering or pre-processing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge