Spectral Distribution Complexity of the Surface Fibrillatory Waves Predicts Post-Catheter Ablation Relapse in Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
Paper and Code
Jan 17, 2024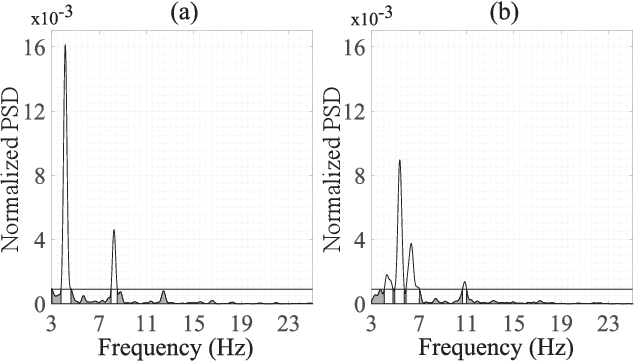
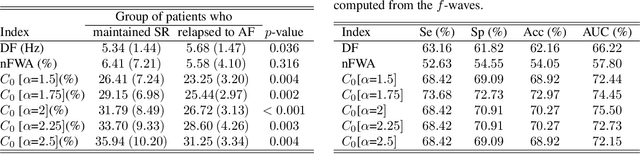
As for most of cardiac arrhythmias, atrial fibrillation (AF) is primarily treated by catheter ablation (CA). However, the mid-term recurrence rate of this procedure in persistent AF patients is still limited and the preoperative prediction of its outcome is clinically interesting to select candidates who could benefit the most from the intervention. This context encouraged the study of C0 complexity as a novel predictor, because it estimates organization of the power spectral distribution (PSD) of the fibrillatory waves (f-waves). For that purpose, the PSD was divided into two divergent components using a threshold, theta, which was considered by multiplying the mean value of the PSD by a factor, alpha, ranging between 1.5 and 2.5. On a database of 74 patients, the values of C0 complexity computed for all alpha factors reported statistically significant differences between the patients who maintained sinus rhythm and those who relapsed to AF after a follow-up of 9 months. They also showed higher values of sensitivity (Se), specificity (Sp), and accuracy (Acc) than the well known predictors of the dominant frequency (DF) and f-wave amplitude. Moreover, the combination of the DF and the C0 complexity computed with alpha = 2, via a decision tree, improved classification until values of Se, Sp and Acc of 75.33, 77.33 and 76.58%, respectively. These results manifests the relevance of the f-wave PSD distribution to anticipate CA outcome in persistent AF patients.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge