Spatiotemporal tomography based on scattered multiangular signals and its application for resolving evolving clouds using moving platforms
Paper and Code
Dec 06, 2020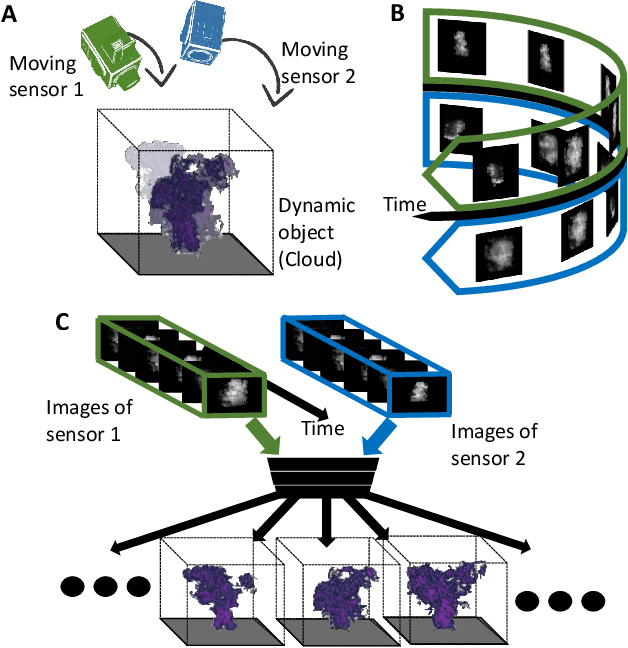
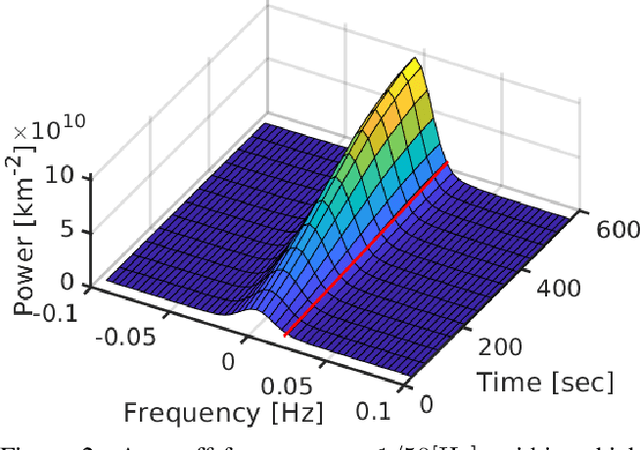
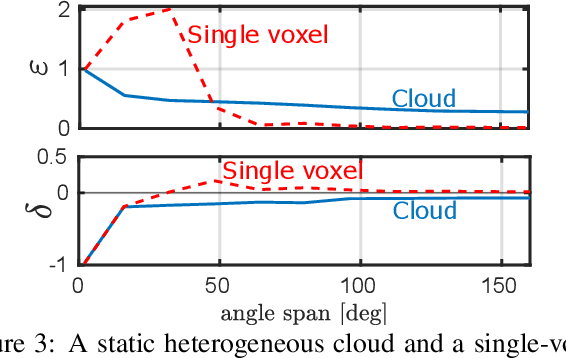
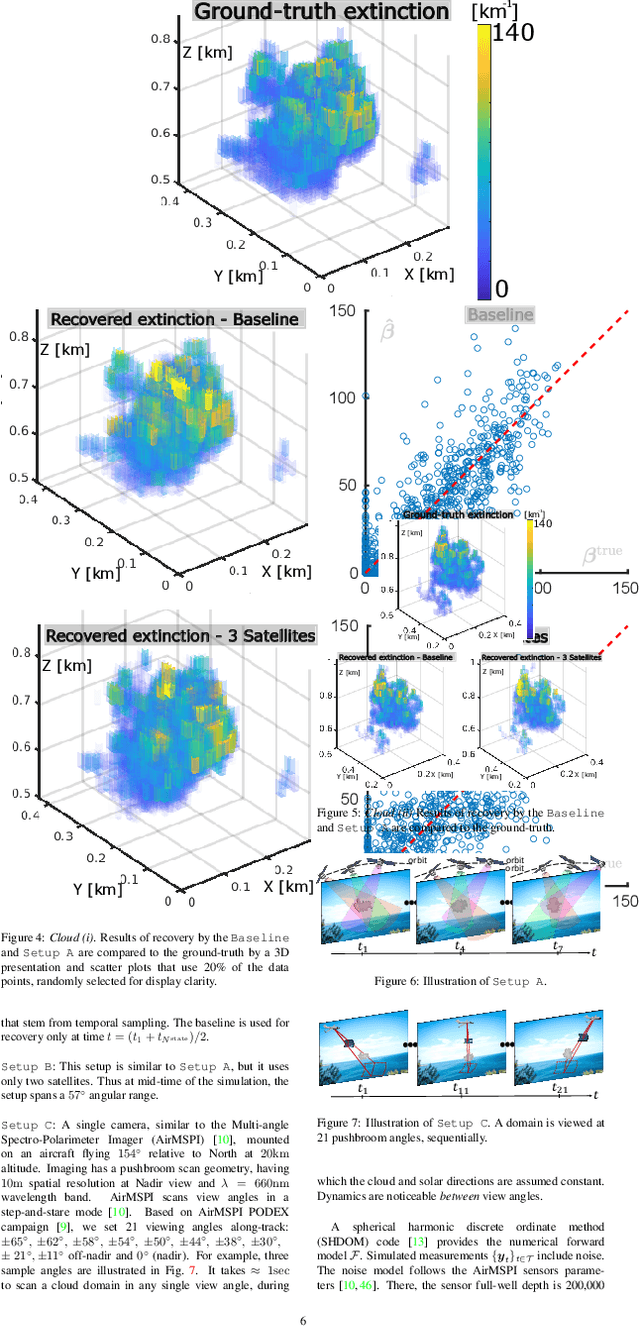
We derive computed tomography (CT) of a time-varying volumetric translucent object, using a small number of moving cameras. We particularly focus on passive scattering tomography, which is a non-linear problem. We demonstrate the approach on dynamic clouds, as clouds have a major effect on Earth's climate. State of the art scattering CT assumes a static object. Existing 4D CT methods rely on a linear image formation model and often on significant priors. In this paper, the angular and temporal sampling rates needed for a proper recovery are discussed. If these rates are used, the paper leads to a representation of the time-varying object, which simplifies 4D CT tomography. The task is achieved using gradient-based optimization. We demonstrate this in physics-based simulations and in an experiment that had yielded real-world data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge