Spatial Modulation with Energy Detection: Diversity Analysis and Experimental Evaluation
Paper and Code
Sep 08, 2023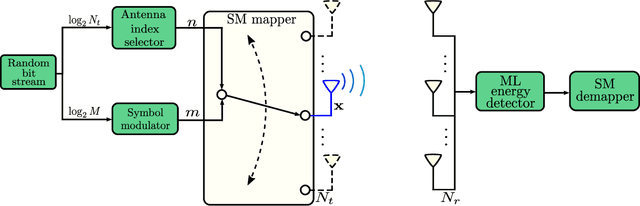
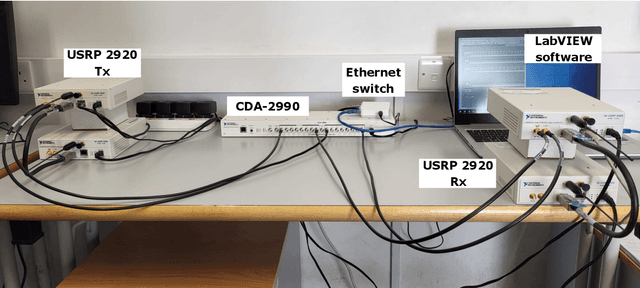
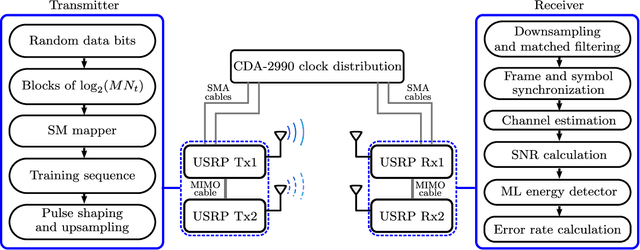
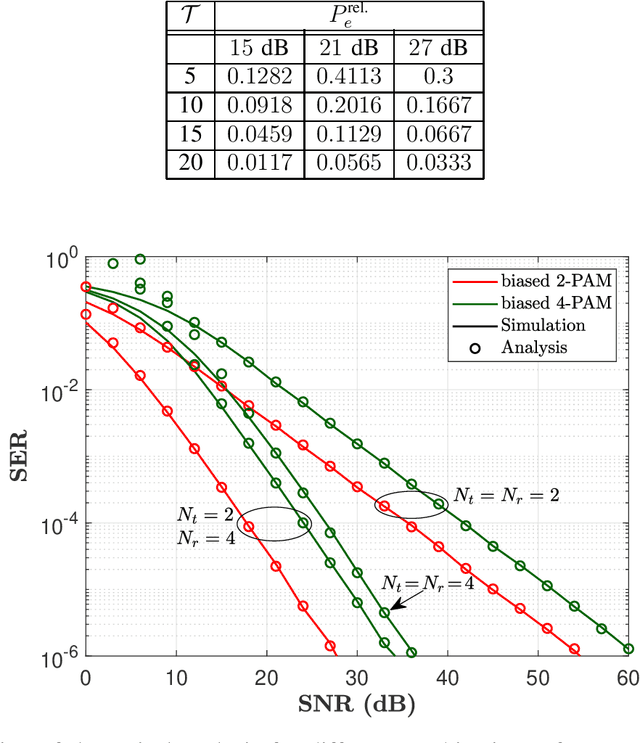
In this paper, we present a non-coherent energy detection scheme for spatial modulation (SM) systems. In particular, the use of SM is motivated by its low-complexity implementation in comparison to multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems, achieved through the activation of a single antenna during transmission. Moreover, energy detection-based communications restrict the channel state information to the magnitude of the fading gains. This consideration makes the design applicable for low-cost low-powered devices since phase estimation and its associated circuitry are avoided. We derive an energy detection metric for a multi-antenna receiver based on the maximum-likelihood (ML) criterion. By considering a biased pulse amplitude modulation, we develop an analytical framework for the SM symbol error rate at high signal-to-noise ratios. Numerical results show that the diversity order is proportional to half the number of receive antennas; this result stems from having partial receiver channel knowledge. In addition, we compare the performance of the proposed scheme with that of the coherent ML receiver and show that the SM energy detector outperforms its coherent counterpart in certain scenarios, particularly when utilizing non-negative constellations. Ultimately, we implement an SM testbed using software-defined radio devices and provide experimental error rate measurements that validate our theoretical contribution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge