Sparse Generative Adversarial Network
Paper and Code
Aug 20, 2019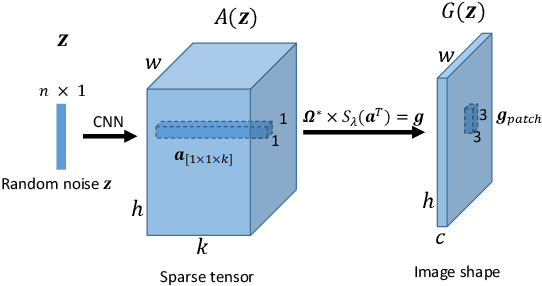
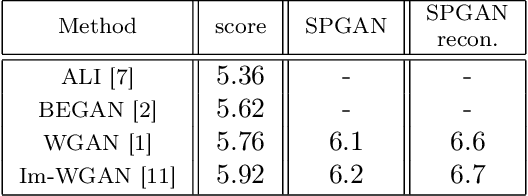
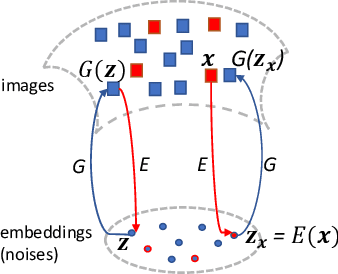
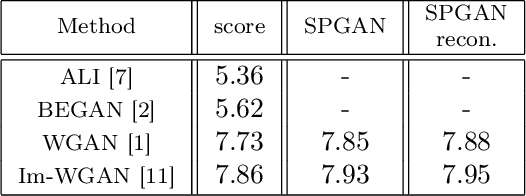
We propose a new approach to Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to achieve an improved performance with additional robustness to its so-called and well recognized mode collapse. We first proceed by mapping the desired data onto a frame-based space for a sparse representation to lift any limitation of small support features prior to learning the structure. To that end we start by dividing an image into multiple patches and modifying the role of the generative network from producing an entire image, at once, to creating a sparse representation vector for each image patch. We synthesize an entire image by multiplying generated sparse representations to a pre-trained dictionary and assembling the resulting patches. This approach restricts the output of the generator to a particular structure, obtained by imposing a Union of Subspaces (UoS) model to the original training data, leading to more realistic images, while maintaining a desired diversity. To further regularize GANs in generating high-quality images and to avoid the notorious mode-collapse problem, we introduce a third player in GANs, called reconstructor. This player utilizes an auto-encoding scheme to ensure that first, the input-output relation in the generator is injective and second each real image corresponds to some input noise. We present a number of experiments, where the proposed algorithm shows a remarkably higher inception score compared to the equivalent conventional GANs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge