Smart Bilingual Focused Crawling of Parallel Documents
Paper and Code
May 23, 2024
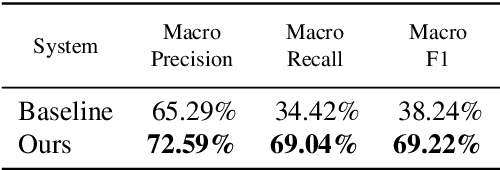

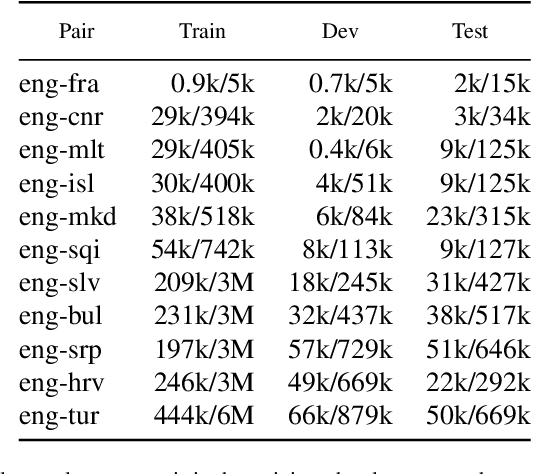
Crawling parallel texts $\unicode{x2014}$texts that are mutual translations$\unicode{x2014}$ from the Internet is usually done following a brute-force approach: documents are massively downloaded in an unguided process, and only a fraction of them end up leading to actual parallel content. In this work we propose a smart crawling method that guides the crawl towards finding parallel content more rapidly. Our approach builds on two different models: one that infers the language of a document from its URL, and another that infers whether a pair of URLs link to parallel documents. We evaluate both models in isolation and their integration into a crawling tool. The results demonstrate the individual effectiveness of both models and highlight that their combination enables the early discovery of parallel content during crawling, leading to a reduction in the amount of downloaded documents deemed useless, and yielding a greater quantity of parallel documents compared to conventional crawling approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge