Slice Tuner: A Selective Data Collection Framework for Accurate and Fair Machine Learning Models
Paper and Code
Mar 10, 2020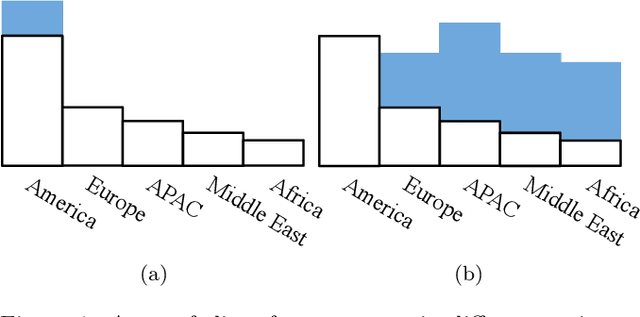
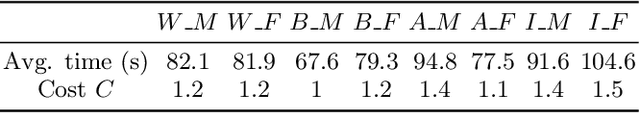
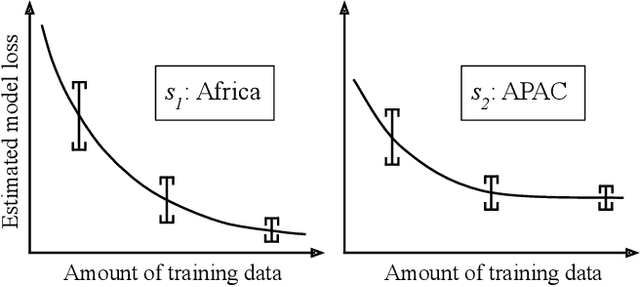
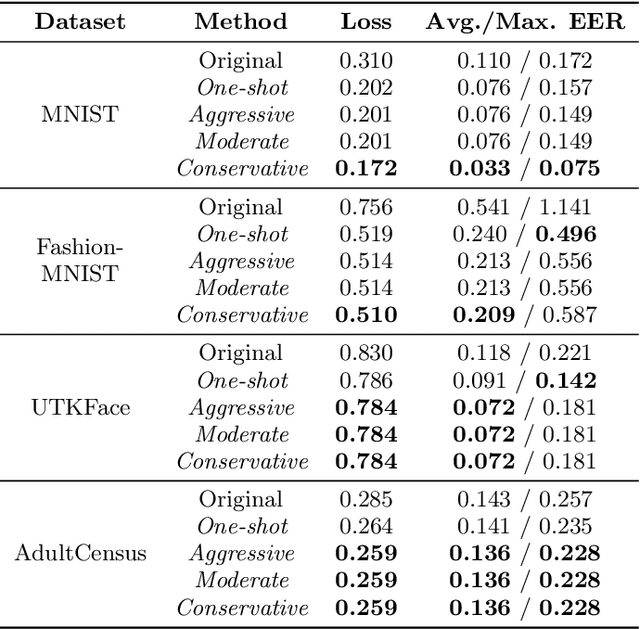
As machine learning becomes democratized in the era of Software 2.0, one of the most serious bottlenecks is collecting enough labeled data to ensure accurate and fair models. Recent techniques including crowdsourcing provide cost-effective ways to gather such data. However, simply collecting data as much as possible is not necessarily an effective strategy for optimizing accuracy and fairness. For example, if an online app store has enough training data for certain slices of data (say American customers), but not for others, collecting more American customer data will only bias the model training. Instead, we contend that one needs to selectively collect data and propose Slice Tuner, which collects possibly-different amounts of data per slice such that the model accuracy and fairness on all slices are optimized. At its core, Slice Tuner maintains learning curves of slices that estimate the model accuracies given more data and uses convex optimization to find the best data collection strategy. The key challenges of estimating learning curves are that they may be inaccurate if there is not enough data, and there may be dependencies among slices where collecting data for one slice influences the learning curves of others. We solve these issues by iteratively and efficiently updating the learning curves as more data is collected. We evaluate Slice Tuner on real datasets using crowdsourcing for data collection and show that Slice Tuner significantly outperforms baselines in terms of model accuracy and fairness, even for initially small slices. We believe Slice Tuner is a practical tool for suggesting concrete action items based on model analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge