SimRec: Mitigating the Cold-Start Problem in Sequential Recommendation by Integrating Item Similarity
Paper and Code
Oct 29, 2024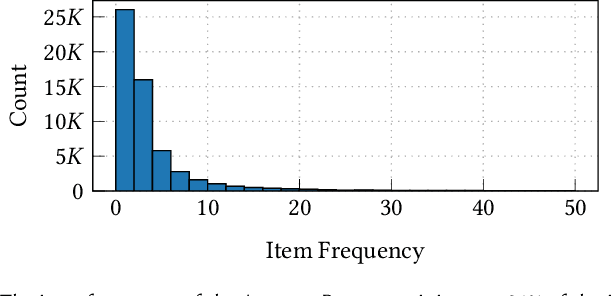

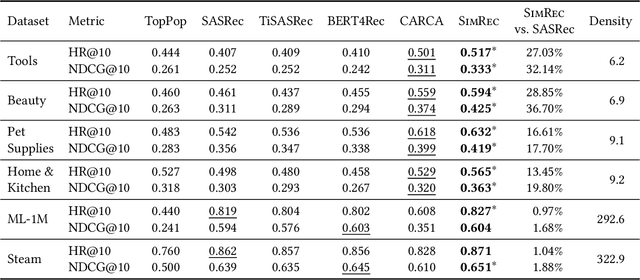
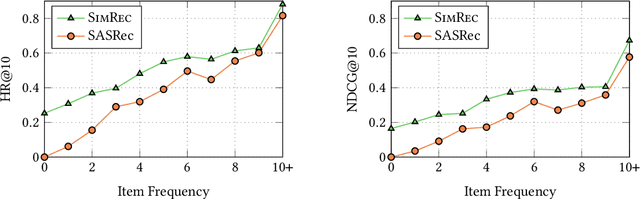
Sequential recommendation systems often struggle to make predictions or take action when dealing with cold-start items that have limited amount of interactions. In this work, we propose SimRec - a new approach to mitigate the cold-start problem in sequential recommendation systems. SimRec addresses this challenge by leveraging the inherent similarity among items, incorporating item similarities into the training process through a customized loss function. Importantly, this enhancement is attained with identical model architecture and the same amount of trainable parameters, resulting in the same inference time and requiring minimal additional effort. This novel approach results in a robust contextual sequential recommendation model capable of effectively handling rare items, including those that were not explicitly seen during training, thereby enhancing overall recommendation performance. Rigorous evaluations against multiple baselines on diverse datasets showcase SimRec's superiority, particularly in scenarios involving items occurring less than 10 times in the training data. The experiments reveal an impressive improvement, with SimRec achieving up to 78% higher HR@10 compared to SASRec. Notably, SimRec outperforms strong baselines on sparse datasets while delivering on-par performance on dense datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/amazon-science/sequential-recommendation-using-similarity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge