Signaling Design for MIMO-NOMA with Different Security Requirements
Paper and Code
Dec 22, 2021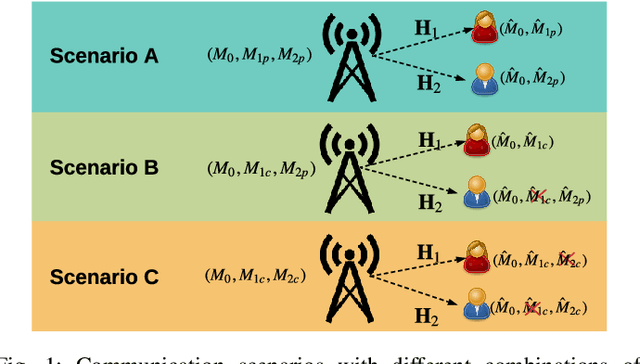
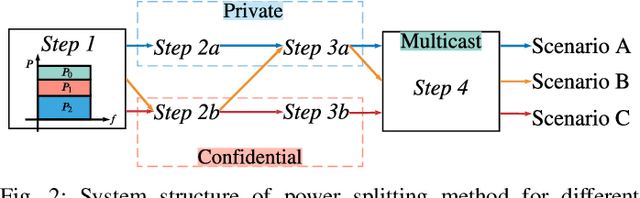
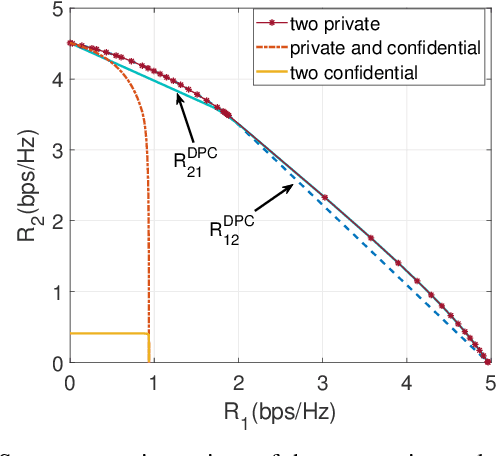
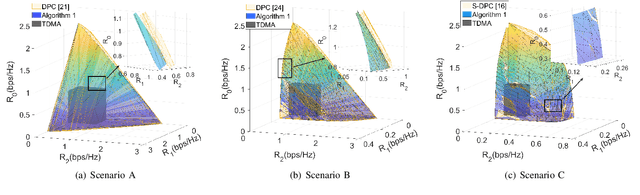
Signaling design for secure transmission in two-user multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) networks is investigated in this paper. The base station broadcasts multicast data to all users and also integrates additional services, unicast data targeted to certain users, and confidential data protected against eavesdroppers. We categorize the above MIMO-NOMA with different security requirements into several communication scenarios. The associated problem in each scenario is nonconvex. We propose a unified approach, called the power splitting scheme, for optimizing the rate equations corresponding to the scenarios. The proposed method decomposes the optimization of the secure MIMO-NOMA channel into a set of simpler problems, including multicast, point-to-point, and wiretap MIMO problems, corresponding to the three basic messages: multicast, private/unicast, and confidential messages. We then leverage existing solutions to design signaling for the above problems such that the messages are transmitted with high security and reliability. Numerical results illustrate the efficacy of the proposed covariance matrix design in secure MIMO-NOMA transmission. The proposed method also outperforms existing solutions, when applicable. In the case of no multicast messages, we also reformulate the nonconvex problem into weighted sum rate (WSR) maximization problems by applying the block successive maximization method and generalizing the zero duality gap. The two methods have their advantages and limitations. Power splitting is a general tool that can be applied to the MIMO-NOMA with any combination of the three messages (multicast, private, and confidential) whereas WSR maximization shows greater potential for secure MIMO-NOMA communication without multicasting. In such cases, WSR maximization provides a slightly better rate than the power splitting method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge