Signal Reconstruction from Quantized Noisy Samples of the Discrete Fourier Transform
Paper and Code
Jan 09, 2022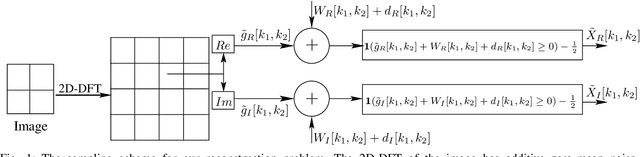

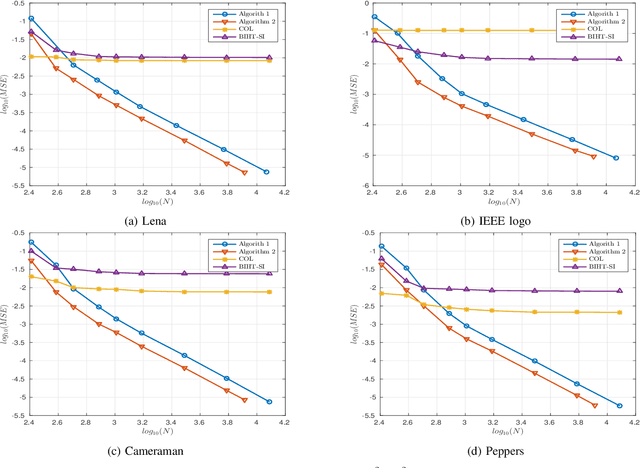
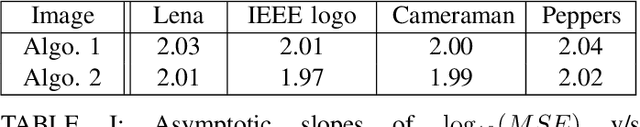
In this paper, we present two variations of an algorithm for signal reconstruction from one-bit or two-bit noisy observations of the discrete Fourier transform (DFT). The one-bit observations of the DFT correspond to the sign of its real part, whereas, the two-bit observations of the DFT correspond to the signs of both the real and imaginary parts of the DFT. We focus on images for analysis and simulations, thus using the sign of the 2D-DFT. This choice of the class of signals is inspired by previous works on this problem. For our algorithm, we show that the expected mean squared error (MSE) in signal reconstruction is asymptotically proportional to the inverse of the sampling rate. The samples are affected by additive zero-mean noise of known distribution. We solve this signal estimation problem by designing an algorithm that uses contraction mapping, based on the Banach fixed point theorem. Numerical tests with four benchmark images are provided to show the effectiveness of our algorithm. Various metrics for image reconstruction quality assessment such as PSNR, SSIM, ESSIM, and MS-SSIM are employed. On all four benchmark images, our algorithm outperforms the state-of-the-art in all of these metrics by a significant margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge