Sequential Modelling with Applications to Music Recommendation, Fact-Checking, and Speed Reading
Paper and Code
Sep 11, 2021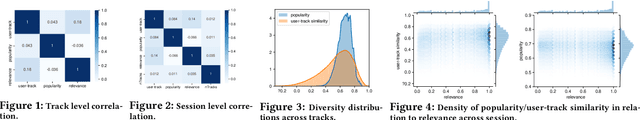
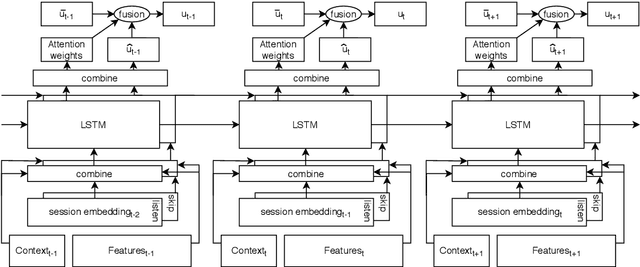
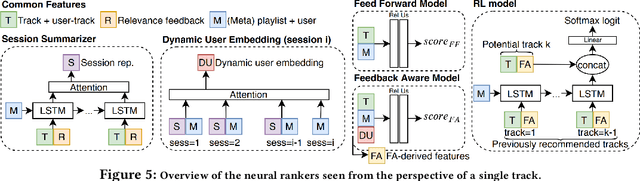
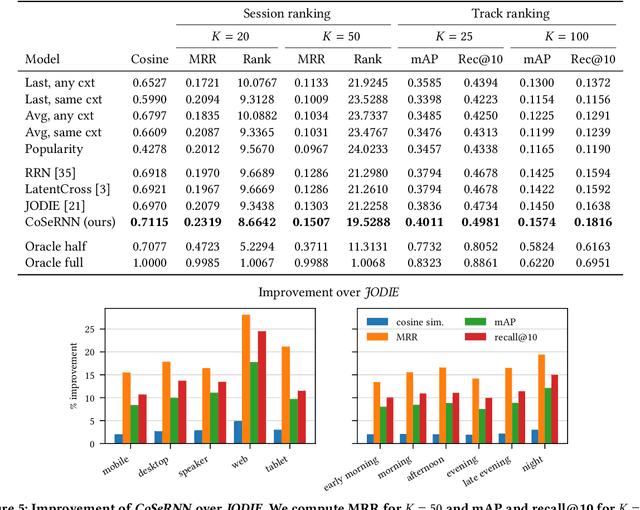
Sequential modelling entails making sense of sequential data, which naturally occurs in a wide array of domains. One example is systems that interact with users, log user actions and behaviour, and make recommendations of items of potential interest to users on the basis of their previous interactions. In such cases, the sequential order of user interactions is often indicative of what the user is interested in next. Similarly, for systems that automatically infer the semantics of text, capturing the sequential order of words in a sentence is essential, as even a slight re-ordering could significantly alter its original meaning. This thesis makes methodological contributions and new investigations of sequential modelling for the specific application areas of systems that recommend music tracks to listeners and systems that process text semantics in order to automatically fact-check claims, or "speed read" text for efficient further classification. (Rest of abstract omitted due to arXiv abstract limit)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge