Sequence-Level Knowledge Distillation for Model Compression of Attention-based Sequence-to-Sequence Speech Recognition
Paper and Code
Nov 12, 2018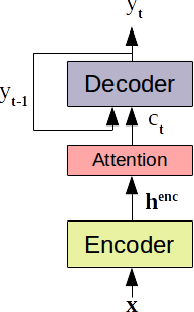

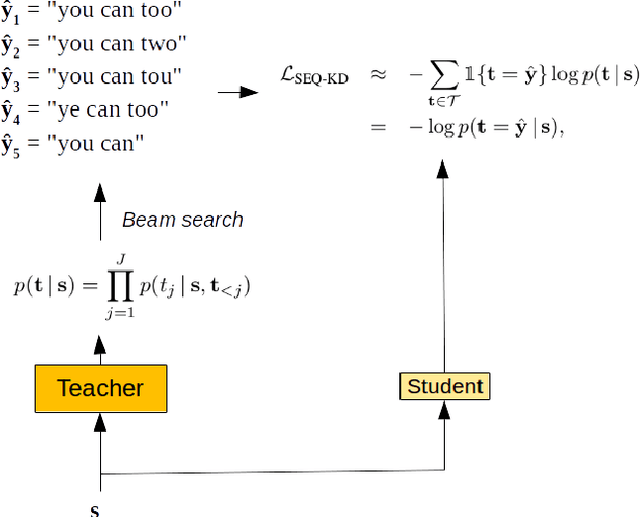
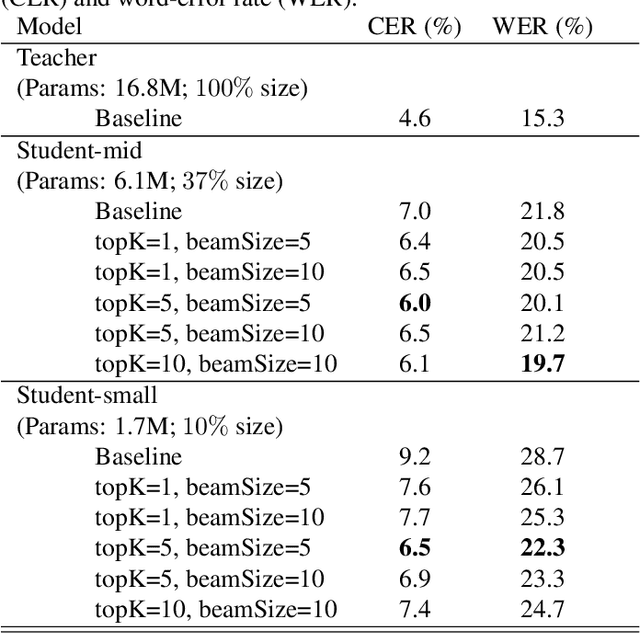
We investigate the feasibility of sequence-level knowledge distillation of Sequence-to-Sequence (Seq2Seq) models for Large Vocabulary Continuous Speech Recognition (LVSCR). We first use a pre-trained larger teacher model to generate multiple hypotheses per utterance with beam search. With the same input, we then train the student model using these hypotheses generated from the teacher as pseudo labels in place of the original ground truth labels. We evaluate our proposed method using Wall Street Journal (WSJ) corpus. It achieved up to $ 9.8 \times$ parameter reduction with accuracy loss of up to 7.0\% word-error rate (WER) increase
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge