Sentence Segmentation in Narrative Transcripts from Neuropsychological Tests using Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Aug 15, 2017
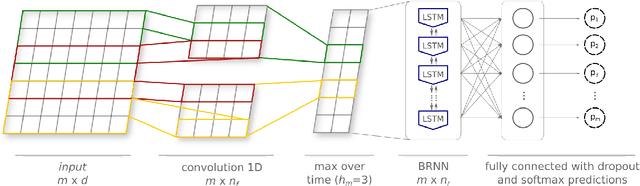
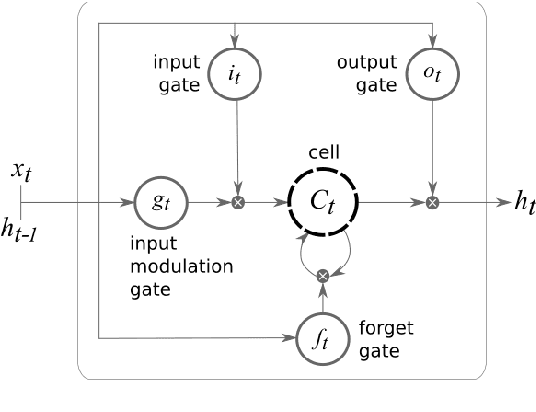
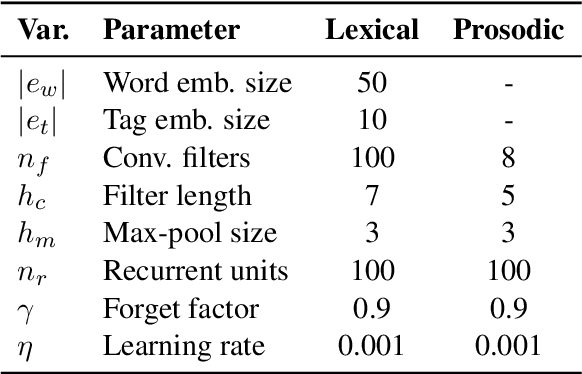
Automated discourse analysis tools based on Natural Language Processing (NLP) aiming at the diagnosis of language-impairing dementias generally extract several textual metrics of narrative transcripts. However, the absence of sentence boundary segmentation in the transcripts prevents the direct application of NLP methods which rely on these marks to function properly, such as taggers and parsers. We present the first steps taken towards automatic neuropsychological evaluation based on narrative discourse analysis, presenting a new automatic sentence segmentation method for impaired speech. Our model uses recurrent convolutional neural networks with prosodic, Part of Speech (PoS) features, and word embeddings. It was evaluated intrinsically on impaired, spontaneous speech, as well as, normal, prepared speech, and presents better results for healthy elderly (CTL) (F1 = 0.74) and Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) patients (F1 = 0.70) than the Conditional Random Fields method (F1 = 0.55 and 0.53, respectively) used in the same context of our study. The results suggest that our model is robust for impaired speech and can be used in automated discourse analysis tools to differentiate narratives produced by MCI and CTL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge