Semi-Supervised Imitation Learning of Team Policies from Suboptimal Demonstrations
Paper and Code
May 11, 2022
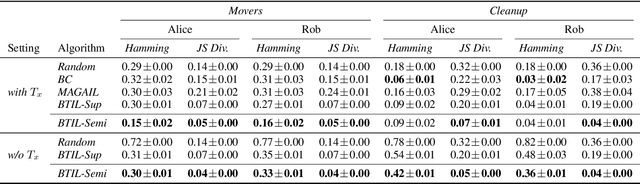
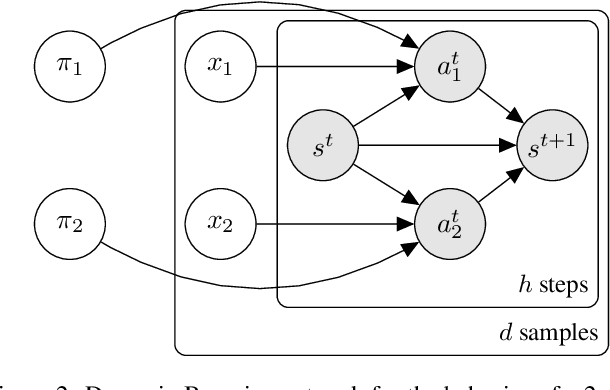
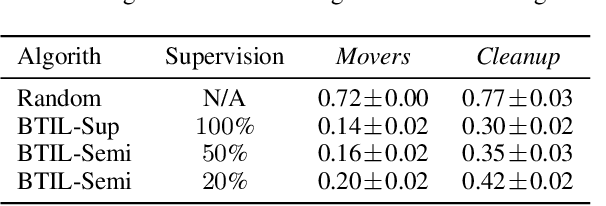
We present Bayesian Team Imitation Learner (BTIL), an imitation learning algorithm to model behavior of teams performing sequential tasks in Markovian domains. In contrast to existing multi-agent imitation learning techniques, BTIL explicitly models and infers the time-varying mental states of team members, thereby enabling learning of decentralized team policies from demonstrations of suboptimal teamwork. Further, to allow for sample- and label-efficient policy learning from small datasets, BTIL employs a Bayesian perspective and is capable of learning from semi-supervised demonstrations. We demonstrate and benchmark the performance of BTIL on synthetic multi-agent tasks as well as a novel dataset of human-agent teamwork. Our experiments show that BTIL can successfully learn team policies from demonstrations despite the influence of team members' (time-varying and potentially misaligned) mental states on their behavior.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge