Semi-supervised acoustic modelling for five-lingual code-switched ASR using automatically-segmented soap opera speech
Paper and Code
Apr 08, 2020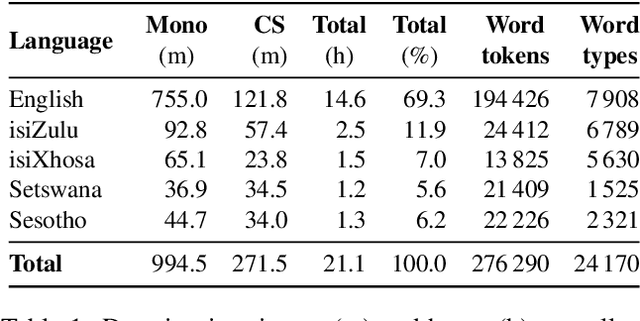
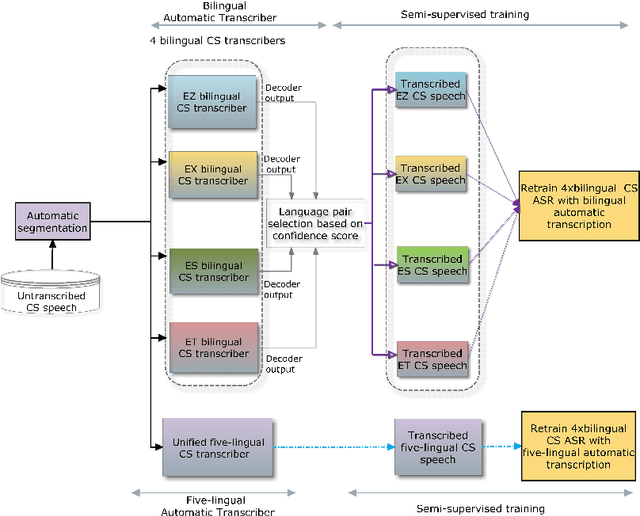

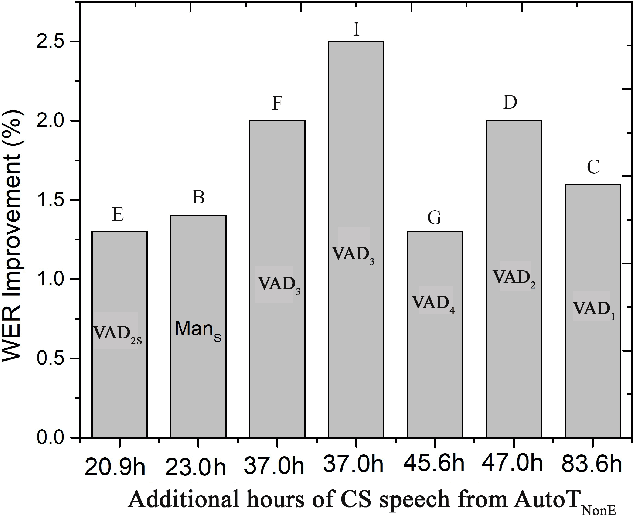
This paper considers the impact of automatic segmentation on the fully-automatic, semi-supervised training of automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems for five-lingual code-switched (CS) speech. Four automatic segmentation techniques were evaluated in terms of the recognition performance of an ASR system trained on the resulting segments in a semi-supervised manner. The system's output was compared with the recognition rates achieved by a semi-supervised system trained on manually assigned segments. Three of the automatic techniques use a newly proposed convolutional neural network (CNN) model for framewise classification, and include a novel form of HMM smoothing of the CNN outputs. Automatic segmentation was applied in combination with automatic speaker diarization. The best-performing segmentation technique was also tested without speaker diarization. An evaluation based on 248 unsegmented soap opera episodes indicated that voice activity detection (VAD) based on a CNN followed by Gaussian mixture modelhidden Markov model smoothing (CNN-GMM-HMM) yields the best ASR performance. The semi-supervised system trained with the resulting segments achieved an overall WER improvement of 1.1% absolute over the system trained with manually created segments. Furthermore, we found that system performance improved even further when the automatic segmentation was used in conjunction with speaker diarization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge