Semantic Mobile Base Station Placement
Paper and Code
Aug 11, 2021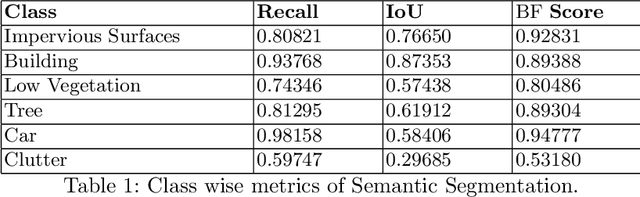

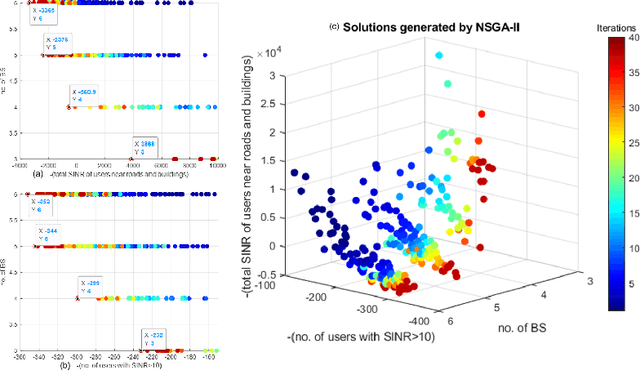

Location of Base Stations (BS) in mobile networks plays an important role in coverage and received signal strength. As Internet ofThings (IoT), autonomous vehicles and smart cities evolve, wireless net-work coverage will have an important role in ensuring seamless connectivity. Due to use of higher carrier frequencies, blockages cause communication to primarily be Line of Sight (LoS), increasing the importance of base station placement. In this paper, we propose a novel placement pipeline in which we perform semantic segmentation of aerial drone imagery using DeepLabv3+ and create its 2.5D model with the help ofDigital Surface Model (DSM). This is used along with Vienna simulator for finding the best location for deploying base stations by formulating the problem as a multi-objective function and solving it using Non-Dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II). The case with and without prior deployed base station is considered. We evaluate the basestation deployment based on Signal to Interference Noise Ratio (SINR)coverage probability and user down-link throughput. This is followed by comparison with other base station placement methods and the bene-fits offered by our approach. Our work is novel as it considers scenarios where there is high ground elevation and building density variation, and shows that irregular BS placement improves coverage.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge