Self-Supervised Learning of Linear Precoders under Non-Linear PA Distortion for Energy-Efficient Massive MIMO Systems
Paper and Code
Oct 13, 2022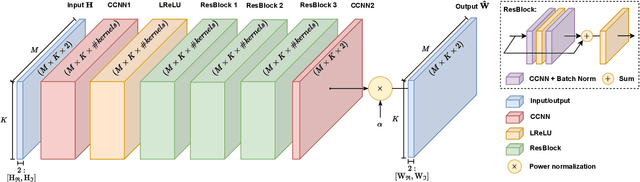
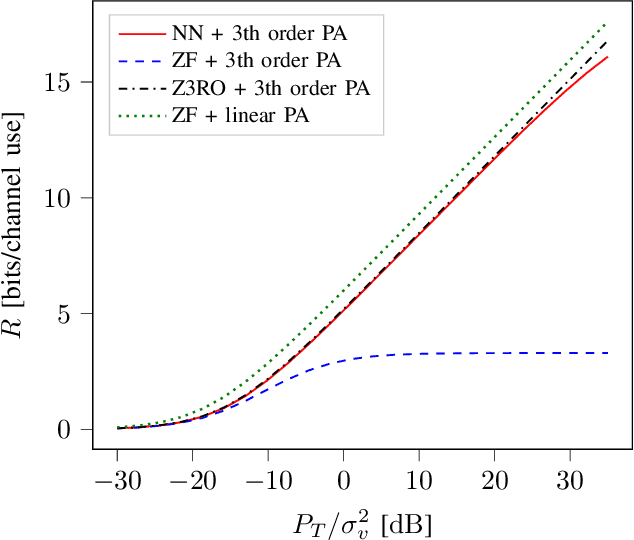
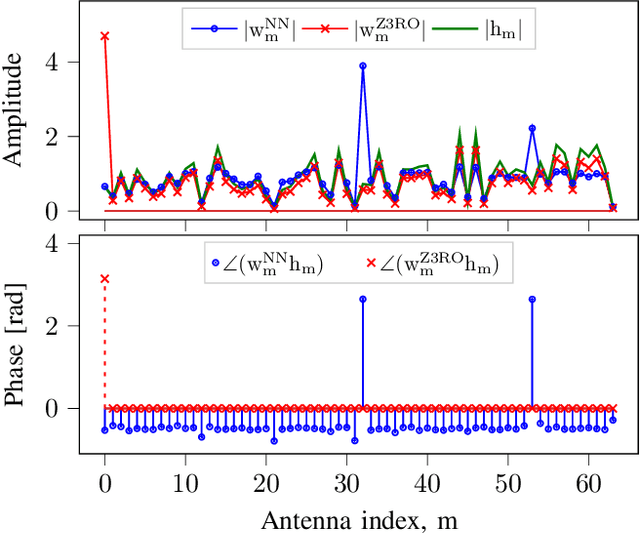

Massive multiple input multiple output (MIMO) systems are typically designed under the assumption of linear power amplifiers (PAs). However, PAs are typically most energy-efficient when operating close to their saturation point, where they cause non-linear distortion. Moreover, when using conventional precoders, this distortion coherently combines at the user locations, limiting performance. As such, when designing an energy-efficient massive MIMO system, this distortion has to be managed. In this work, we propose the use of a neural network (NN) to learn the mapping between the channel matrix and the precoding matrix, which maximizes the sum rate in the presence of this non-linear distortion. This is done for a third-order polynomial PA model for both the single and multi-user case. By learning this mapping a significant increase in energy efficiency is achieved as compared to conventional precoders and even as compared to perfect digital pre-distortion (DPD), in the saturation regime.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge