Segmentation of Ink and Parchment in Dead Sea Scroll Fragments
Paper and Code
Nov 16, 2024
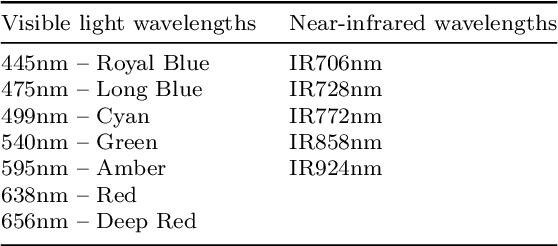
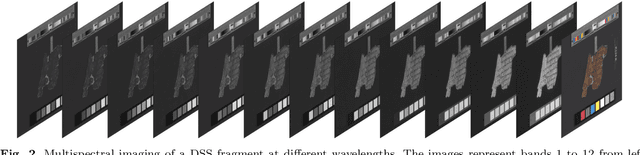
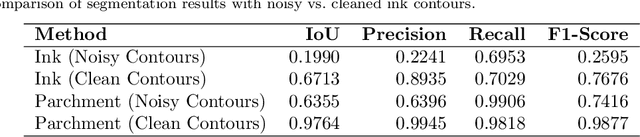
The discovery of the Dead Sea Scrolls over 60 years ago is widely regarded as one of the greatest archaeological breakthroughs in modern history. Recent study of the scrolls presents ongoing computational challenges, including determining the provenance of fragments, clustering fragments based on their degree of similarity, and pairing fragments that originate from the same manuscript -- all tasks that require focusing on individual letter and fragment shapes. This paper presents a computational method for segmenting ink and parchment regions in multispectral images of Dead Sea Scroll fragments. Using the newly developed Qumran Segmentation Dataset (QSD) consisting of 20 fragments, we apply multispectral thresholding to isolate ink and parchment regions based on their unique spectral signatures. To refine segmentation accuracy, we introduce an energy minimization technique that leverages ink contours, which are more distinguishable from the background and less noisy than inner ink regions. Experimental results demonstrate that this Multispectral Thresholding and Energy Minimization (MTEM) method achieves significant improvements over traditional binarization approaches like Otsu and Sauvola in parchment segmentation and is successful at delineating ink borders, in distinction from holes and background regions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge