Seed-Point Based Geometric Partitioning of Nuclei Clumps
Paper and Code
Apr 12, 2018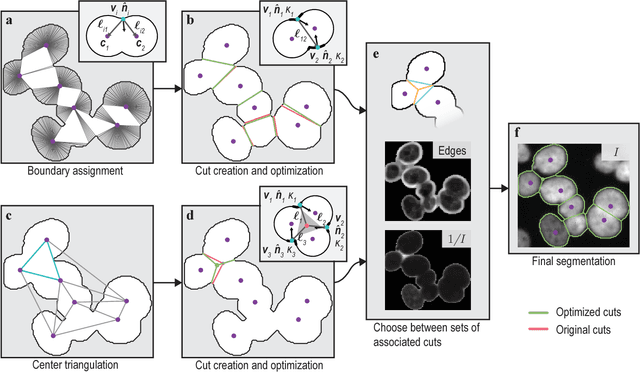
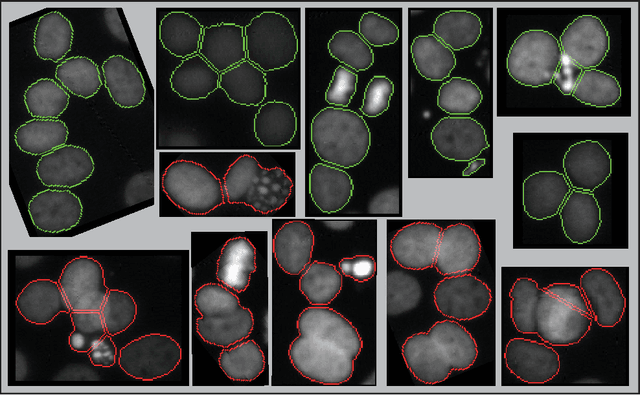
When applying automatic analysis of fluorescence or histopathological images of cells, it is necessary to partition, or de-clump, partially overlapping cell nuclei. In this work, I describe a method of partitioning partially overlapping cell nuclei using a seed-point based geometric partitioning. The geometric partitioning creates two different types of cuts, cuts between two boundary vertices and cuts between one boundary vertex and a new vertex introduced to the boundary interior. The cuts are then ranked according to a scoring metric, and the highest scoring cuts are used. This method was tested on a set of 2420 clumps of nuclei and was found to produced better results than current popular analysis software.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge