Secrecy Performance of Small-Cell Networks with Transmitter Selection and Unreliable Backhaul under Spectrum Sharing Environment
Paper and Code
Mar 07, 2021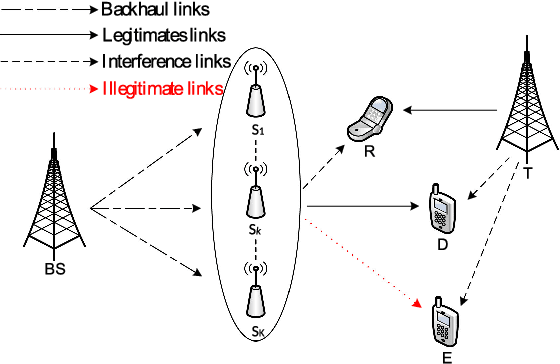
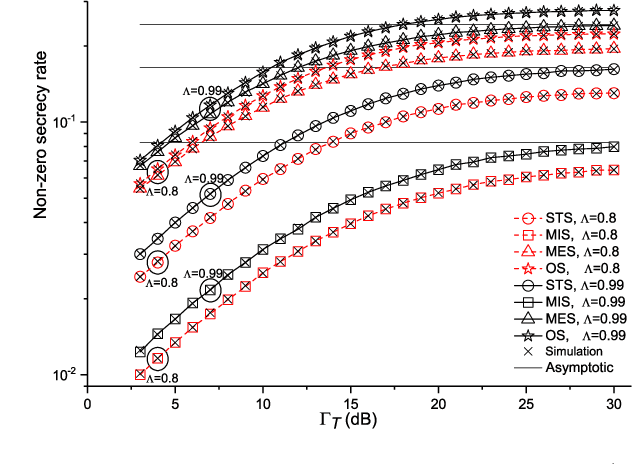
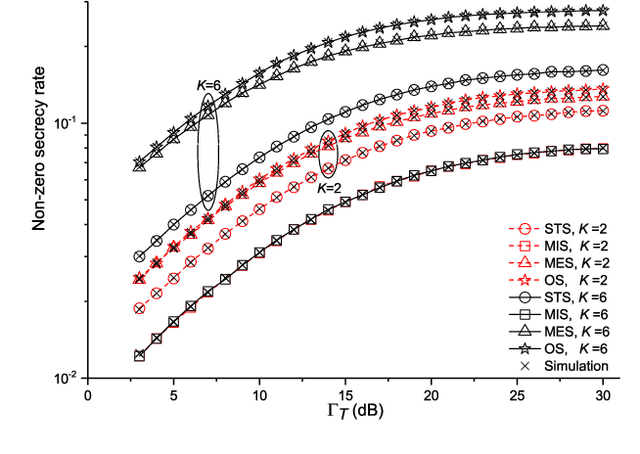
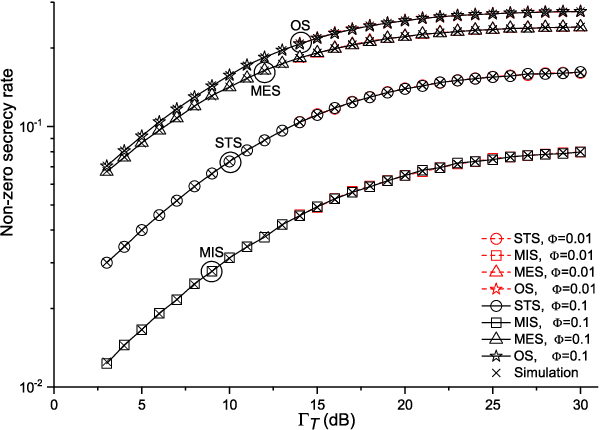
We investigate the secrecy performance of an underlay small-cell cognitive radio network under unreliable backhaul connections. The small-cell network shares the same spectrum with the primary network, ensuring that a desired outage probability constraint is always met in the primary network. {To improve the security of the small-cell cognitive network, we propose three sub-optimal small-cell transmitter selection schemes,} namely sub-optimal transmitter selection, minimal interference selection, and minimal eavesdropping selection. Closed-form expressions of the non-zero secrecy rate, secrecy outage probability, and ergodic secrecy capacity are provided for the schemes along with asymptotic expressions. {We also propose an optimal selection scheme and compare performances with the sub-optimal selection schemes.} {Computable expressions for the non-zero secrecy rate and secrecy outage probability are presented for the optimal selection scheme.} Our results show that by increasing the primary transmitter's power and the number of small-cell transmitters, the system performance improves. The selection scheme, the backhaul reliability, and the primary user quality-of-service constraint also have a significant impact on secrecy performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge