Scaling up graph homomorphism for classification via sampling
Paper and Code
Apr 08, 2021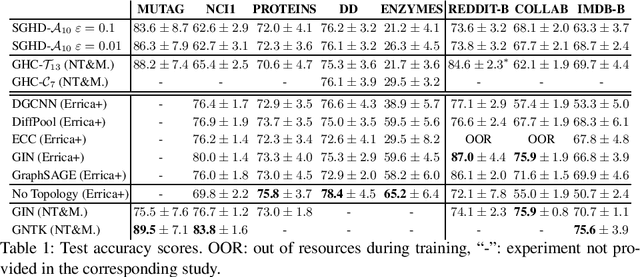
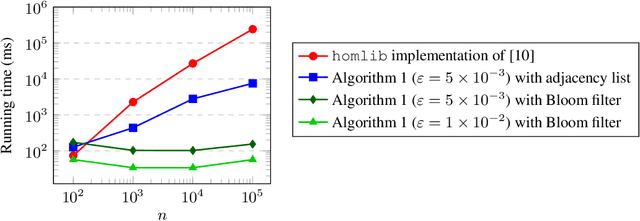
Feature generation is an open topic of investigation in graph machine learning. In this paper, we study the use of graph homomorphism density features as a scalable alternative to homomorphism numbers which retain similar theoretical properties and ability to take into account inductive bias. For this, we propose a high-performance implementation of a simple sampling algorithm which computes additive approximations of homomorphism densities. In the context of graph machine learning, we demonstrate in experiments that simple linear models trained on sample homomorphism densities can achieve performance comparable to graph neural networks on standard graph classification datasets. Finally, we show in experiments on synthetic data that this algorithm scales to very large graphs when implemented with Bloom filters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge