Saliency-Guided Mutual Learning Network for Few-shot Fine-grained Visual Recognition
Paper and Code
May 12, 2023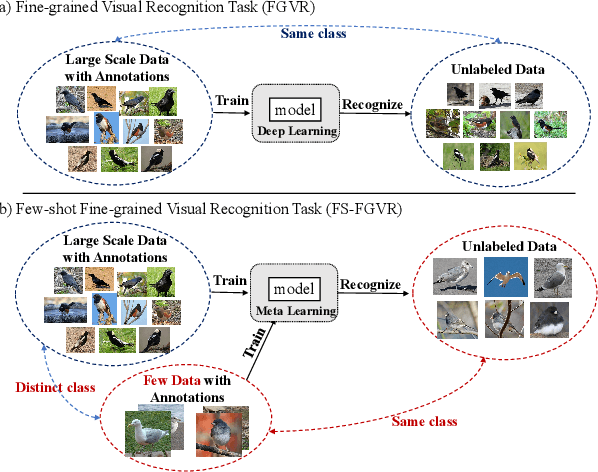
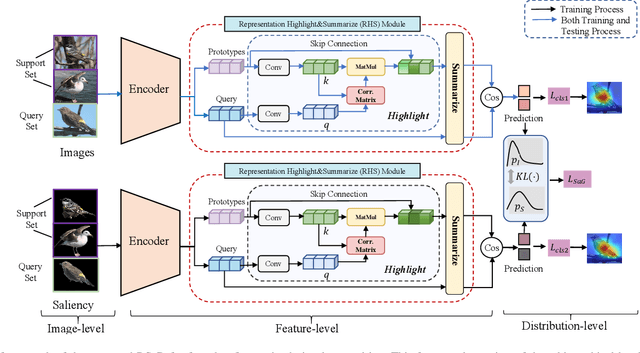
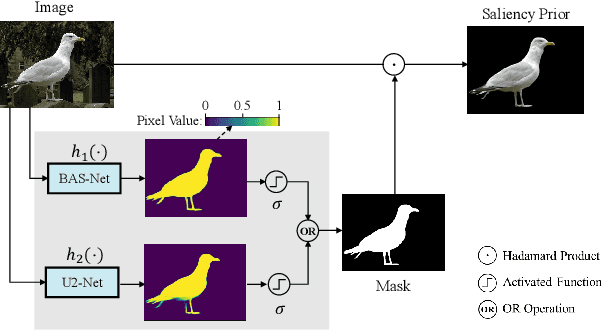
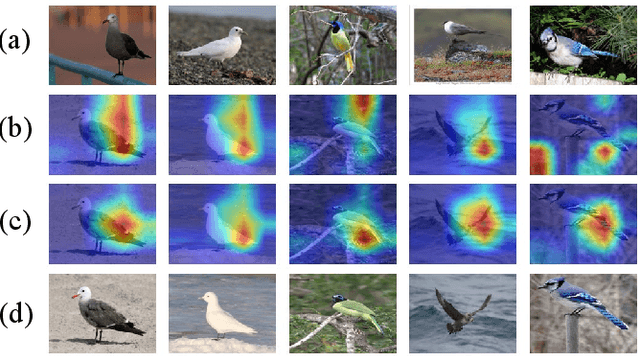
Recognizing novel sub-categories with scarce samples is an essential and challenging research topic in computer vision. Existing literature focus on addressing this challenge through global-based or local-based representation approaches. The former employs global feature representations for recognization, which may lack fine-grained information. The latter captures local relationships with complex structures, possibly leading to high model complexity. To address the above challenges, this article proposes a novel framework called SGML-Net for few-shot fine-grained visual recognition. SGML-Net incorporates auxiliary information via saliency detection to guide discriminative representation learning, achieving high performance and low model complexity. Specifically, SGML-Net utilizes the saliency detection model to emphasize the key regions of each sub-category, providing a strong prior for representation learning. SGML-Net transfers such prior with two independent branches in a mutual learning paradigm. To achieve effective transfer, SGML-Net leverages the relationships among different regions, making the representation more informative and thus providing better guidance. The auxiliary branch is excluded upon the transfer's completion, ensuring low model complexity in deployment. The proposed approach is empirically evaluated on three widely-used benchmarks, demonstrating its superior performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge