Role of Intonation in Scoring Spoken English
Paper and Code
Aug 23, 2018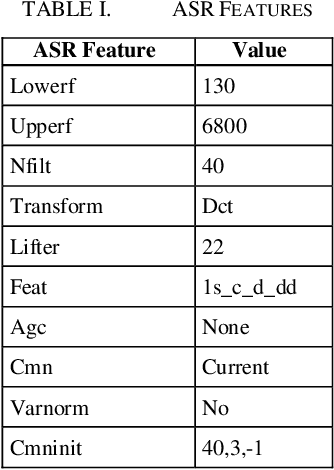
In this paper, we have introduced and evaluated intonation based feature for scoring the English speech of nonnative English speakers in Indian context. For this, we created an automated spoken English scoring engine to learn from the manual evaluation of spoken English. This involved using an existing Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) engine to convert the speech to text. Thereafter, macro features like accuracy, fluency and prosodic features were used to build a scoring model. In the process, we introduced SimIntonation, short for similarity between spoken intonation pattern and "ideal" i.e. training intonation pattern. Our results show that it is a highly predictive feature under controlled environment. We also categorized interword pauses into 4 distinct types for a granular evaluation of pauses and their impact on speech evaluation. Moreover, we took steps to moderate test difficulty through its evaluation across parameters like difficult word count, average sentence readability and lexical density. Our results show that macro features like accuracy and intonation, and micro features like pause-topography are strongly predictive. The scoring of spoken English is not within the purview of this paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge