Robust Latent Representations via Cross-Modal Translation and Alignment
Paper and Code
Nov 03, 2020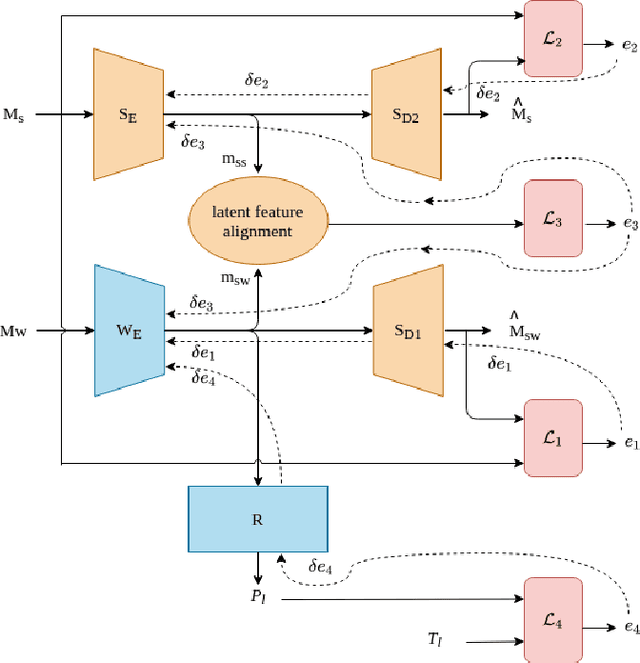


Multi-modal learning relates information across observation modalities of the same physical phenomenon to leverage complementary information. Most multi-modal machine learning methods require that all the modalities used for training are also available for testing. This is a limitation when the signals from some modalities are unavailable or are severely degraded by noise. To address this limitation, we aim to improve the testing performance of uni-modal systems using multiple modalities during training only. The proposed multi-modal training framework uses cross-modal translation and correlation-based latent space alignment to improve the representations of the weaker modalities. The translation from the weaker to the stronger modality generates a multi-modal intermediate encoding that is representative of both modalities. This encoding is then correlated with the stronger modality representations in a shared latent space. We validate the proposed approach on the AVEC 2016 dataset for continuous emotion recognition and show the effectiveness of the approach that achieves state-of-the-art (uni-modal) performance for weaker modalities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge