Robust and efficient computation of retinal fractal dimension through deep approximation
Paper and Code
Jul 12, 2022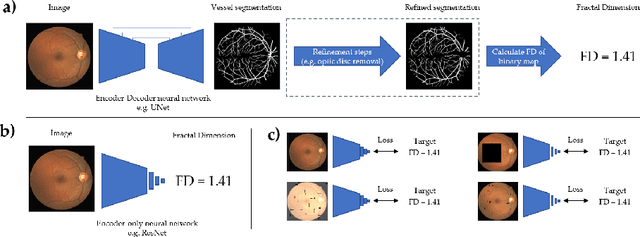

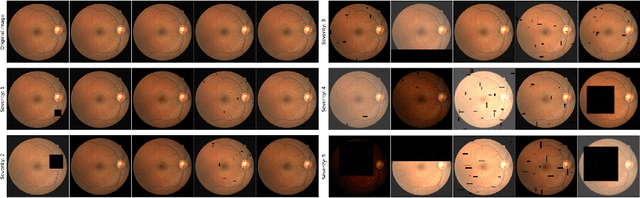
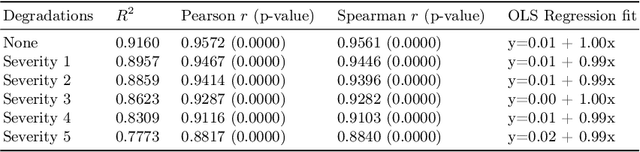
A retinal trait, or phenotype, summarises a specific aspect of a retinal image in a single number. This can then be used for further analyses, e.g. with statistical methods. However, reducing an aspect of a complex image to a single, meaningful number is challenging. Thus, methods for calculating retinal traits tend to be complex, multi-step pipelines that can only be applied to high quality images. This means that researchers often have to discard substantial portions of the available data. We hypothesise that such pipelines can be approximated with a single, simpler step that can be made robust to common quality issues. We propose Deep Approximation of Retinal Traits (DART) where a deep neural network is used predict the output of an existing pipeline on high quality images from synthetically degraded versions of these images. We demonstrate DART on retinal Fractal Dimension (FD) calculated by VAMPIRE, using retinal images from UK Biobank that previous work identified as high quality. Our method shows very high agreement with FD VAMPIRE on unseen test images (Pearson r=0.9572). Even when those images are severely degraded, DART can still recover an FD estimate that shows good agreement with FD VAMPIRE obtained from the original images (Pearson r=0.8817). This suggests that our method could enable researchers to discard fewer images in the future. Our method can compute FD for over 1,000img/s using a single GPU. We consider these to be very encouraging initial results and hope to develop this approach into a useful tool for retinal analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge